Why use Playwright for Mobile Testing?
Playwright brings a set of pragmatic advantages that translate directly to better mobile testing:
- Reliable, deterministic automation: built in waiting and modern async primitives reduce flaky timing errors and make tests more stable.
- Device emulation out of the box: viewport, device pixel ratio, user agent, touch support, geolocation and locale can be emulated so you can validate responsive layouts quickly. Emulation is fast to configure and cheap to run in CI.
- Cross-engine coverage with one API: Chromium, WebKit and Firefox are accessible through the same API, making it easy to run identical tests across desktop and mobile rendering engines.
- Modern interaction set: Playwright supports touch gestures, swipes, pinches, drag and drop, network throttling and offline simulation, which are essential for realistic mobile scenarios.
Why add MCP to Playwright?
Playwright gives you execution speed and fidelity. MCP brings intent and context. Together they change how tests are written and maintained:
- Intent driven tests: write high level steps like click the login button or complete checkout and let the model pick the correct element, reducing selector plumbing.
- Contextual element resolution: MCP sends a rich, structured representation of the page state to an LLM, enabling the model to infer elements even when IDs or classes change. This raises resilience against UI churn.
- Natural language diagnostics: Instead of a cryptic selector failure, the model can explain why it chose an element or why an action looks ambiguous, speeding up debugging.
- Faster test creation and maintenance: Initial flows can be generated from a plain language description and the AI can update steps when the UI evolves, reducing ongoing maintenance effort.
Those benefits make MCP a force multiplier for Playwright when testing mobile web and hybrid web views. But how does that work across Android and iOS in practice?
Why Playwright MCP does not fully solve Native Mobile App Testing
Playwright MCP significantly improves mobile web and hybrid testing, but it is not designed to be a complete solution for native mobile apps. This limitation is structural, not incremental, and it matters when teams move beyond web views into real native user journeys.
- Native UI trees are outside Playwright’s execution model
Playwright operates on browser engines and web rendering contexts. Even with MCP adding intelligence on top, the execution layer still fundamentally understands HTML, DOM, CSS, and web events. Native mobile apps expose UI trees through platform specific accessibility layers, not through the DOM. MCP can reason about intent, but Playwright cannot execute actions on native UI elements it cannot see or control.
- OS level interactions are first class in native apps
Native mobile flows depend on OS level constructs such as system dialogs, permissions, biometric prompts, deep links, background to foreground transitions, and app lifecycle events. These are not web concepts. Playwright MCP can describe intent like allow location access, but without native hooks it cannot reliably execute or validate these steps.
- Visual similarity does not equal semantic control
MCP can use visual and semantic context to infer elements, but in native apps the same visual component can represent very different underlying controls across iOS, Android, React Native, or Flutter. Without direct access to native metadata, actions remain probabilistic rather than deterministic, which is risky for visual regression and release gating.
- Real device fragmentation increases complexity
True native QA requires validation across device models, OS versions, OEM skins, and hardware capabilities. Playwright MCP can orchestrate logic, but it still depends on external native tooling to actually run and validate those flows on real devices at scale.
In short, Playwright MCP is excellent at making web automation intelligent. It is not designed to replace native mobile automation frameworks.
How Panto AI Solves The Broken Mobile QA Problem
| Feature | Playwright MCP | Panto QA |
| Primary scope | Web centric automation with intent driven element resolution | Full spectrum mobile QA including native, hybrid and web |
| Strength | Fast execution, unified API, LLM powered resilience | Native UI hooks, deterministic exports, no code authoring |
| Native app coverage | Web views and web centric flows; can orchestrate native tools via MCP | Direct native automation on iOS and Android with native element access |
| Web view support | First class: attach to WebView and run Playwright pages | Full support and orchestration with native and web actions |
| Device execution | Emulators, remote browsers, ADB connected Android; device clouds via integrations | Real device farms, BrowserStack/LambdaTest integrations, on prem device farms |
| Test authoring | Intent based plain language with model assisted generation | No code visual authoring plus deterministic script export |
| Self healing | Model guided element resolution reduces flakiness; healing via retries and re-resolution | Built in AI self healing with continuous learning and recovery logs |
| Deterministic script export | Possible but centered on Playwright flows | Exports to Appium or Maestro for audit and portability |
| CI/CD integration | Fast CI smoke tests and regression; costs tied to LLM calls | Enterprise CI integration at scale with parallel real device runs |
| Best fit | Mobile web, PWAs, hybrid apps where web view is primary | End to end mobile QA for native heavy apps and enterprise scale testing |
Implementing Playwright MCP: Practical Steps
Adopting Playwright MCP requires planning, environment setup, MCP integration, and switching to intent-based testing.
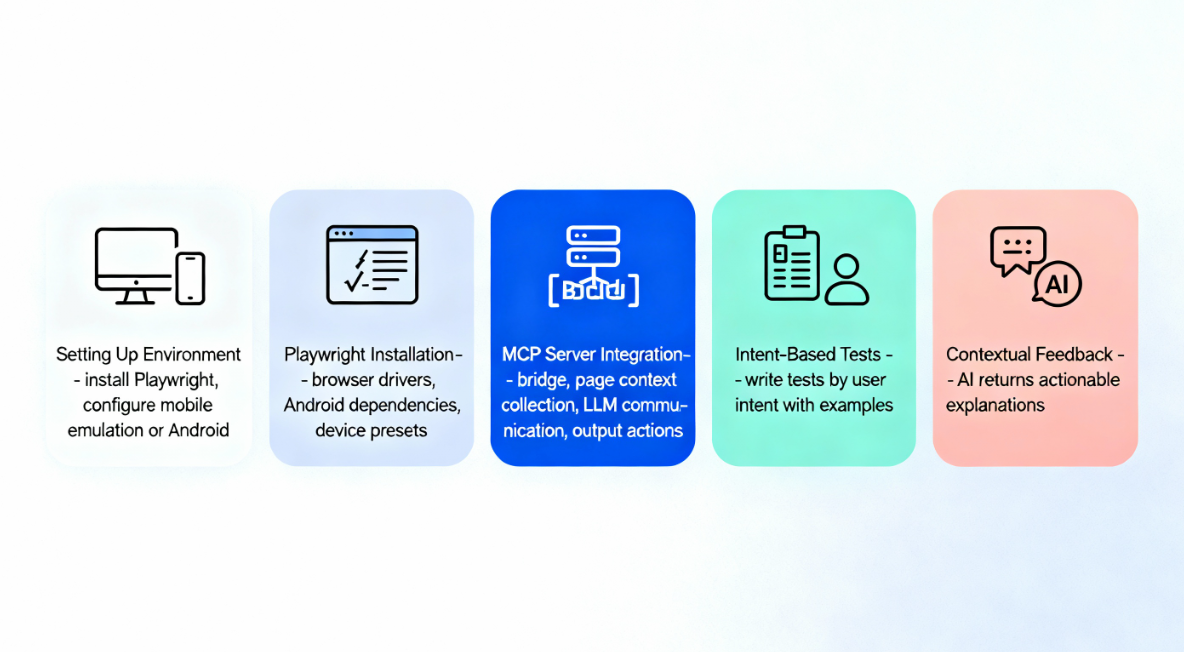
1. Setting Up the Environment
Install Playwright and configure mobile emulation or Android support. Ensure the execution layer is working before adding AI.
2. Playwright Installation and Configuration
Install Playwright with browser drivers. For Android, install Playwright’s Android dependencies.
Configure device presets with viewport and user agent settings.
3. MCP Server Integration
The MCP server is the bridge between Playwright and the LLM. It:
- Collects Playwright page context
- Formats context for the LLM
- Sends/receives LLM decisions
- Outputs executable Playwright actions
Often, this is done via a plugin or library.
4. Designing Intent-Based Tests
The biggest shift: test creation based on user intent, not selectors.
Examples:
- “Navigate to the product page and add the first item to the cart.”
- “Complete checkout using the saved payment method.”
- “Verify that the mobile menu contains ‘My Account.’”
5. Leveraging Contextual Feedback
Instead of generic errors, LLMs can return actionable explanations, such as conflicting element labels or ambiguous instructions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, Playwright MCP comes with considerations.
LLM Dependency and Cost
Relying on LLMs introduces:
- Latency
- API pricing
- Dependency on model performance
Optimizing context is key.
The Native Mobile Gap
True end-to-end native mobile testing still requires an additional tool for now. Playwright MCP is ideal for teams focused on mobile web and hybrid applications.
Conclusion: The Future of Intelligent Mobile QA
The integration of Playwright and MCP marks a major evolution in mobile QA. This combination advances beyond brittle scripts toward intelligent, context-aware automation.
Key Takeaways
- Resilience: AI element detection reduces flakiness
- Efficiency: Unified API + intent-based scripts accelerate testing
- Scope: Strong coverage for mobile web and hybrid apps
Playwright MCP makes mobile web testing faster, smarter, and more inclusive.
- AI handles selectors, test-writing, and recovery.
- Teams keep pace with rapid UI changes.
- Maintenance demands plunge.
- Releases speed up.
Limitations exist for fully native apps. Use MCP for mobile web, and pair with native tools like Appium or comprehensive platforms like Panto AI for complete coverage. Strategic use of Playwright MCP improves test reliability, increases team collaboration, and delivers enterprise-grade mobile test automation.
FAQ’s
Q: What is Playwright MCP in mobile testing?
Playwright MCP combines :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}’s browser automation engine with a Model Context Protocol (MCP) layer that enables intent-driven, LLM-assisted test execution. Playwright handles deterministic browser control, while MCP interprets high-level instructions (such as “complete checkout”) and resolves elements using contextual understanding rather than rigid selectors.
Q: Can Playwright MCP test mobile apps?
It depends on the app type. Playwright MCP supports mobile web applications, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), and hybrid apps with WebViews. It does not support fully native iOS and Android apps without external tooling. Because Playwright operates in browser contexts, it cannot directly access native UI trees.
Q: How does Playwright support mobile app automation?
Playwright supports mobile automation through device emulation (viewport, DPR, user agent), touch event simulation, network throttling, offline mode, Android device automation via ADB, and WebView attachment for hybrid apps. It does not natively control iOS UIKit or Android native view hierarchies.
Q: What is the difference between Playwright MCP and standard Playwright?
Standard :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1} uses selector-driven tests, deterministic DOM targeting, and manual test authoring with explicit error messages. Playwright MCP enables intent-driven tests, context-aware element inference, LLM-assisted test generation, and natural-language diagnostics. MCP reduces brittle selector maintenance but introduces LLM dependency.
Q: Can Playwright MCP replace Appium for Android or iOS testing?
No. :contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2} interacts directly with native accessibility trees on iOS and Android, whereas Playwright MCP does not have native UI hooks. Playwright MCP is ideal for mobile web, hybrid apps, and WebView-heavy flows. For native-first applications, Appium or similar frameworks remain necessary.
Q: How does Playwright MCP handle Android app testing?
Playwright can connect to Android devices via ADB, attach to WebViews inside apps, and run browser-context automation. However, it cannot directly manipulate native Android UI elements such as permission dialogs or system-level prompts without external native automation support.
Q: Is Playwright MCP suitable for iOS app testing?
Only for web content. :contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3} supports WebKit-based automation and mobile Safari emulation, but it does not directly automate native iOS UI components such as biometric prompts, system permission dialogs, or native navigation stacks. Full native iOS automation requires platform-native tools.
Q: What are the main benefits of using MCP with Playwright?
Key benefits include reduced selector fragility, context-aware element resolution, faster test authoring, natural-language debugging feedback, and improved resilience against UI churn. MCP shifts testing from “find this CSS selector” toward “achieve this user goal,” increasing abstraction and adaptability.
Q: What are the limitations of Playwright MCP in enterprise mobile QA?
Constraints include LLM latency and API cost, model decision variability, limited native app control, increased governance requirements for release gating, and dependency on structured context formatting. MCP improves intelligence but does not eliminate the need for deterministic validation layers.
Q: When should teams choose Playwright MCP vs a native mobile QA platform?
Choose Playwright MCP when your application is web-first or hybrid, you need fast CI smoke tests, UI churn causes selector instability, or you prefer intent-based authoring. Choose a native-first platform when your app is heavily native, OS-level flows are critical, real-device fragmentation testing is required, or release gating depends on deterministic native validation. Many mature teams combine both approaches.






