Vibe Debugging is revolutionizing how developers identify and resolve software issues by capturing rich, contextual traces across user interactions, system states, and code execution paths.
Unlike traditional debugging, which relies on isolated logs or breakpoints, Vibe Debugging provides a holistic view of what happened, when, and why—enabling faster, more accurate root cause analysis.
This guide outlines the best practices to maximize effectiveness, security, and team alignment when using Vibe Debugging in modern development environments.
Understanding the Vibe Debugging Workflow
Every Vibe Debugging session follows three core stages: Capture, Analyze, and Resolve.
Capture focuses on gathering contextual data. Analyze interprets that data to find root causes. Resolve implements fixes and verifies them in context.
Breaking down each stage into clear steps helps maintain consistency and maximize the tool’s capabilities. Whether you’re troubleshooting a frontend UI glitch or a backend error, adhering to a structured workflow speeds up resolution and minimizes regressions.
1. Configure Contextual Triggers
Contextual triggers define when vibe debugging starts recording detailed traces. Set these thoughtfully:
- Error-based triggers: Configure auto-capture when unhandled exceptions occur. This ensures you never miss stack traces or environment details.
- Performance thresholds: Use triggers for slow API responses or rendering times. Capturing trace data around performance anomalies uncovers bottlenecks faster.
- User interactions: For elusive UI bugs, attach triggers to specific actions like form submissions or button clicks. This lets you record relevant state and events around the glitch.
Avoid overtriggering, which can flood your storage and make logs unwieldy. Focus on high-value scenarios to keep traces concise.
2. Limit Captured Scope
While vibe debugging can record extensive context, capturing everything at once creates noise. Narrow the scope:
- Selective modules: Identify the application modules most likely tied to the issue. Limit tracing to those modules instead of global instrumentation.
- Time windows: Configure your session to record only around the trigger event—five seconds before and after, for example. This yields targeted insights without hours of irrelevant logs.
- Environment filters: Differentiate between development, staging, and production. Restrict verbose captures to non-production environments or high-severity incidents only.
Scoping captures proactively reduces pull request times and storage costs while delivering clean, focused logs.
3. Annotate Critical Code Paths
Annotations guide vibe debugging into capturing custom rules. Use in-code markers to:
- Highlight entry points: Mark key functions or API handlers that should be traced deeply. Custom annotations ensure it captures local variables and state snapshots.
- Add business context: When debugging domain logic, annotate steps with business-level descriptions. This helps non-technical stakeholders follow the trace when reviewing.
- Tag asynchronous flows: For code using callbacks, promises, or async/await, use annotations to track continuation contexts. This prevents losing trace continuity across threads.
Well-placed annotations augment vibe debugging’s automated context, enabling quicker correlations between events and application logic.
4. Leverage Real-Time Collaboration
Vibe Debugging excels when teams collaborate on live sessions. Adopt these collaboration strategies:
- Shared sessions: Invite teammates to your active session so they can monitor logs and contribute observations in real time. This is invaluable when reproducing intermittent bugs.
- In-session comments: Use a comment feature to flag interesting events or attach screenshots. This provides a narrative timeline of the debugging process.
- Role-based views: Segregate views for developers, QA, and product managers. Each stakeholder can focus on relevant data—stack traces for devs, user flows for PMs, and test outcomes for QA.
Real-time teamwork accelerates consensus on root causes and prevents siloed troubleshooting. Also, looking into AI vs Traditional QA can really make a difference in solving problems within one’s codebase, aiding vibe debugging.
5. Embrace Responsible AI Debugging
To use vibe debugging effectively, follow these AI-specific best practices:
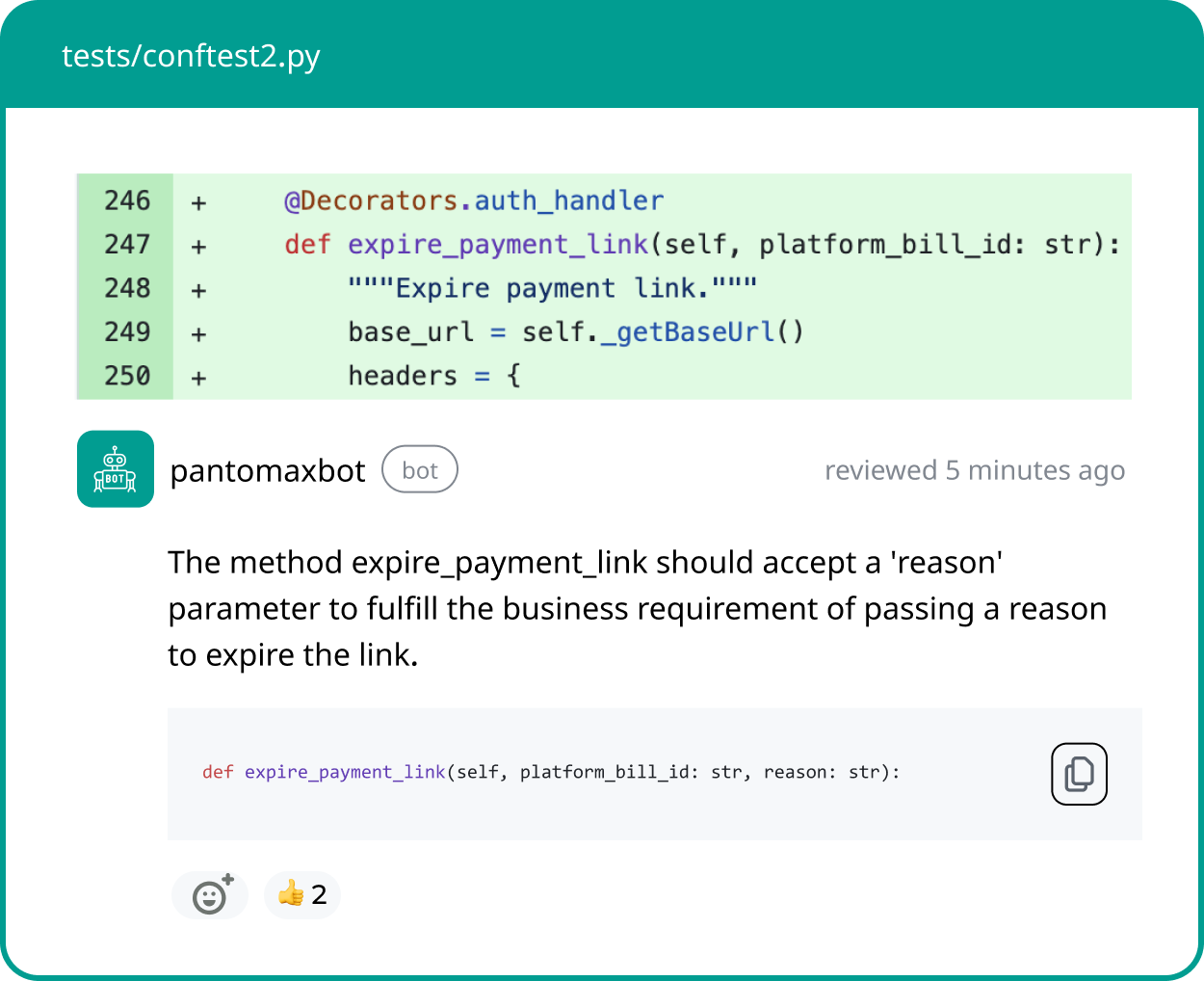
- Always review code suggestions: Never blindly accept AI-generated code changes. Read them, reason through them, and ensure they make logical sense before merging.
- Use focused prompts: Instead of “fix the code,” describe the exact bug. For example: “Fix the form submission error when the input is empty.”
- Integrate with version control: Make each AI fix a separate Git commit. This enables easy rollback and side-by-side diffing to track changes.
- Connect to CI/CD and test automation: AI debugging must live inside a feedback loop. Run unit and functional tests against AI fixes before merging to ensure stability.
- Educate your team: Ensure everyone understands how to prompt, review, and own AI-generated code. This builds a culture of accountability.
- Don’t skip learning: Use AI suggestions as an opportunity to grow. Study the fix, understand the logic, and document it. Avoid treating AI as a black box.
By embedding AI into disciplined workflows, Vibe Debugging becomes not just fast, but safe, maintainable, and empowering.
6. Choose the Right Vibe Debugging Tools
The right tooling makes Vibe Debugging feel natural and effective. Here are the leading platforms:
- Panto AI – As we’re building the world’s first end-to-end Vibe Debugging Platform, Panto AI hopes to bring code review, AI-driven development and test automation, and conversational debugging together into one seamless, intelligent workflow for development teams.
- Cursor – Tailor-made for vibe workflows, Cursor offers in-editor AI suggestions, refactoring, and inline debugging support across large codebases.
- Replit AI – A lightweight, web-based environment that supports real-time AI pair programming and instant feedback.
- Bolt – Built for collaborative development, Bolt integrates prompts, debugging help, and deployment pipelines for seamless team workflows.
- Gemini Code Assist – Ideal for Android or web developers, it integrates with IDEs and supports natural language bug fixes.
Choose the tool that aligns with your tech stack, team size, and deployment model.
7. Integrate with CI/CD Pipelines
To catch regressions early, embed vibe debugging into your build and release process:
- Pre-deploy sanity checks: Trigger captures on critical smoke tests or integration tests in CI/CD. Automated traces allow you to analyze failures before they reach production.
- Post-deploy monitoring: Configure the run lightweight monitors on key endpoints after deployment. Capture only error rates or latency spikes to minimize overhead.
- Alerting and rollbacks: Connect alerts to your notification channels. If a session captures a high-severity error, automatically block the release or trigger a rollback workflow.
Seamless CI/CD integration ensures debugging capabilities are part of your everyday development cycle.
8. Analyze with Contextual Dashboards
Rather than sifting raw logs, use dashboard features to visualize patterns:
- Trace heatmaps: Identify hotspots in your code by viewing aggregated trace durations. This reveals slow functions or external calls that dominate execution time.
- User journey timelines: Map user interactions to backend events. When a user reports an issue, you can jump directly to that timeline and see the precise sequence of events.
- Error frequency charts: Track the recurrence of exceptions over time. Correlate spikes with recent deployments, code changes, or environmental factors.
Dashboards turn complex traces into actionable insights at a glance.
9. Adopt Iterative Debug Loops
Vibe debugging is most effective when used iteratively:
- Hypothesize: Based on initial traces, form a theory about the cause. Use code annotations or configuration tweaks to test small changes.
- Capture again: Run a new session focused on the updated code path. Compare before-and-after traces to validate your fix.
- Validate: Confirm the issue is resolved under multiple scenarios. Use automated tests or manual QA to ensure robustness.
- Document: Archive the session and your findings. Over time, this builds an internal knowledge base of common issues and their resolutions.
Iterative loops refine your understanding quickly and reduce the likelihood of introducing new bugs.
10. Secure Sensitive Data
Vibe debugging captures rich context, which may include sensitive information. Protect user privacy and compliance:
- Data masking: Configure vibe debugging to automatically obfuscate PII, credentials, and tokens in trace data.
- Access controls: Use role-based access to session logs. Ensure only authorized personnel can view sensitive fields.
- Retention policies: Define how long sessions are stored before automatic deletion. Align retention with your organization’s data governance policies.
Proactive data security maintains compliance and builds trust with stakeholders and end users.
11. Optimize Storage and Costs
Storing large volumes of trace data can be expensive. Control costs by:
- Sampling: Use sampling rates to capture a representative subset of sessions. Focus full data capture on high-severity incidents.
- Compression: Enable built-in trace compression to reduce payload sizes without losing critical details.
- Archival tier : Move older or lower-priority sessions to cost-effective storage buckets. Retrieve them on demand if needed.
Balancing data fidelity and storage efficiency keeps your debug platform sustainable.
12. Share Knowledge Across Teams
Vibe debugging sessions serve as training and documentation assets:
- Debug playbooks: Extract common patterns and root causes into team playbooks. Reference previous sessions as examples.
- Onboarding: New hires can explore past sessions to understand system architecture, typical issues, and resolution workflows.
- Cross-functional demos: Showcase relevant sessions in stakeholder meetings. Demonstrating real traces helps bridge the gap between engineering and product or support teams.
Leveraging recordings as knowledge artifacts multiplies their value beyond a single debug session.
Conclusion
Mastering Vibe Debugging transforms error diagnosis from guesswork into a precise, data-driven process. By configuring targeted triggers, scoping captures, annotating code paths, and leveraging collaborative workflows, teams accelerate root cause analysis and build resilient applications.
With various vibe debugging tools up and coming, developers now have the option to make debugging faster, smarter, and deeply contextual. Implement these best practices to elevate your debugging workflow and deliver higher-quality software faster.