Mobile apps dominate today’s digital economy. More than 76 percent of US adults shop on smartphones, and for many businesses, the mobile app is the primary customer touchpoint. Quality is no longer a nice to have. It is existential.
Industry research reinforces this reality. A Tricentis study found that 42 percent of companies consider mobile app quality critical to competitive advantage, while 39 percent link it directly to user retention. Poor mobile experiences translate directly into churn, negative reviews, and lost revenue.
Yet despite this pressure, most mobile teams still rely heavily on manual QA to validate releases. As AI agents enter software testing, a fundamental question emerges.
Will manual QA survive, or is agentic AI testing set to replace it?
Definition: Manual QA vs AI Testing
Manual QA refers to human testers executing test cases by interacting with an application directly, validating functionality, usability, and visual behavior without automated scripts.
AI testing, particularly agentic AI testing, uses autonomous software agents that analyze applications, generate test scenarios, execute them independently, and adapt based on outcomes using machine learning and computer vision.
This article examines manual QA vs AI debugging through the lens of mobile development and explores what QA looks like by 2030.
The Current Role of Manual QA in Mobile Testing
Manual QA remains foundational in many mobile teams today.
Human testers excel at:
- Exploratory testing
- Usability and UX validation
- New feature validation
- Subjective judgment calls that require empathy
Testers emulate real user behavior, notice visual inconsistencies, and explore unexpected flows. These strengths explain why manual QA persists even in teams with automation.
However, manual QA carries structural limitations that become acute as teams scale.
Structural Limitations of Manual QA
- Speed constraints
Manual testing is slow by nature. Navigating dozens of screens across devices takes time that CI/CD pipelines do not have. - Human error
Repetitive testing leads to fatigue and oversight. Even experienced testers miss edge cases under pressure. - Coverage gaps
No human team can simultaneously test hundreds of device and OS combinations. - High operational cost
Scaling coverage requires hiring more testers, not improving efficiency.
In modern CI and CD environments, these limitations create release friction.
Why Manual QA Breaks Down in CI/CD Pipelines
Continuous integration assumes fast, repeatable validation. Manual QA fundamentally conflicts with this assumption.
Key Bottlenecks
Slow feedback loops
Manual QA testing introduces delays between code completion and validation. Developers wait hours or days for results.
Limited parallelism
Human testers cannot match the parallel execution possible in device farms or cloud infrastructure.
Context switching cost
Delayed feedback forces developers to revisit old code, increasing cognitive load and fix time.
Collaboration friction
Agile teams stall while waiting for test completion, reducing overall velocity.
As BrowserStack notes, manual testing in Agile pipelines is tedious and creates a time gap between development and release readiness.
The Rise of Agentic AI Testing
AI driven testing is evolving beyond scripted automation into agentic systems that behave more like digital QA teammates.
What Is an AI Testing Agent?
An AI testing agent is autonomous software that:
- Observes application behavior
- Decides what actions to take
- Learns from outcomes
- Adapts test strategies over time
Unlike traditional automation, agents are not bound to predefined scripts.
How Agentic AI Testing Works
1. Application Understanding
Agents map UI elements using computer vision and semantic analysis. Screens, buttons, inputs, and user flows are identified without manual locators.
2. Action Selection
Instead of following scripts, agents choose actions based on learned behavior. They explore paths likely to expose bugs, including edge cases.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Advanced agents learn from failures and successes, refining future test strategies.
4. Self Healing
When UI changes, agents adapt rather than fail, updating internal models automatically.
This autonomy distinguishes agentic testing from traditional automation frameworks.
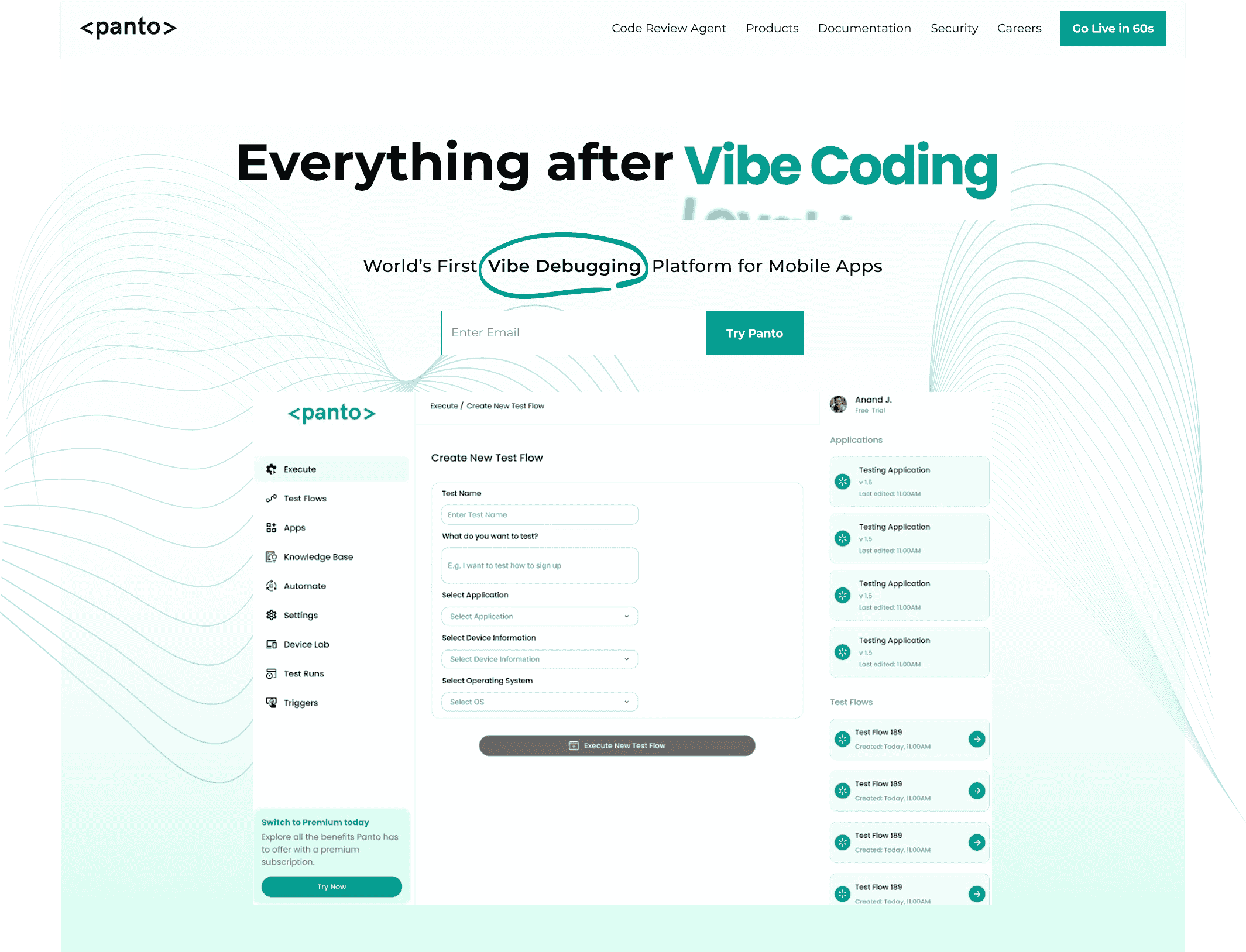
Everything After Vibe Coding
Panto AI helps developers find, explain, and fix bugs faster with AI-assisted QA—reducing downtime and preventing regressions.
- ✓ Explain bugs in natural language
- ✓ Create reproducible test scenarios in minutes
- ✓ Run scripts and track issues with zero AI hallucinations
Market Momentum Behind AI Testing
The shift is not theoretical. Market data confirms it.
- The AI-powered testing market grew from USD 414.7M in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1.63B by 2030 at 18.4 percent CAGR.
- The broader AI agent market is forecast to grow from USD 5.1B in 2024 to USD 47.1B by 2030.
- QA skill profiles are shifting rapidly, with AI and ML proficiency rising sharply among testers.
These trends signal a structural change, not a tooling fad.
Manual QA vs Agentic AI Testing: A Comparison
| Dimension | Manual QA | Agentic AI Testing |
| Speed | Slow | Near real time |
| Coverage | Limited | Broad and combinatorial |
| Scalability | Linear with headcount | Scales with compute |
| Maintenance | Human intensive | Self adapting |
| CI/CD fit | Poor | Native |
| Cost efficiency | Low at scale | High at scale |
Manual QA provides depth in narrow areas. Agentic AI provides breadth and speed.
What Mobile Testing Looks Like in 2030
By 2030, QA evolves into Quality Engineering.
1. Expected Characteristics
- AI driven risk scoring highlights high risk modules daily
- Autonomous agents generate and execute tests continuously
- Tests are scheduled dynamically based on cost and infrastructure availability
- Developers receive real time quality feedback in IDEs
- Production monitoring feeds back into test generation
- Human testers act as quality strategists, not click operators
Testing becomes continuous, adaptive, and data driven.
2. Organizational Impact
Skills Evolution
Manual testing skills remain relevant, but AI literacy becomes essential. QA engineers shift toward analysis, orchestration, and code governance.
Cost Structure
Upfront investment in AI infrastructure is offset by long term efficiency gains and reduced manual overhead.
Speed to Market
Validation cycles shrink dramatically, enabling more frequent releases with lower risk.
Where Panto AI Fits Conceptually
Some platforms are positioning themselves around agent driven QA that integrates tightly with developer workflows.
The core idea is not replacing humans, but removing friction between code changes and quality validation. AI agents operate continuously, while humans guide strategy and interpret critical failures.
This hybrid model reflects where the industry is heading.
Key Takeaways
- Traditional or manual QA is not disappearing, but its role is shrinking
- Agentic AI testing addresses scale, speed, and coverage gaps
- The future of QA is hybrid, not purely human or purely automated
- Teams that delay adoption risk slower releases and higher costs
Conclusion: Preparing for an Agent Driven Future
The era of manual QA as the primary quality gate is ending. By 2030, QA becomes an intelligence driven discipline supported by autonomous agents.
The choice facing engineering leaders is not whether AI will enter QA, but how deliberately it will be integrated.
Teams that invest early in platforms going for agentic testing and skill transformation will ship faster, with higher confidence, and lower operational drag.






