What Is Native Mobile App Testing?
Native app testing is the process of evaluating mobile applications built specifically for a single operating system, to ensure they function correctly, perform well, and deliver exceptional user experiences.
These applications leverage device-specific hardware and software features like cameras, GPS, push notifications, and biometric sensors to provide seamless, high-performance experiences tailored to each platform.
Unlike hybrid or web applications that run across multiple platforms with a single codebase, native apps require platform-specific testing strategies because each operating system has unique UI conventions, hardware configurations, API behaviors, and user expectations.
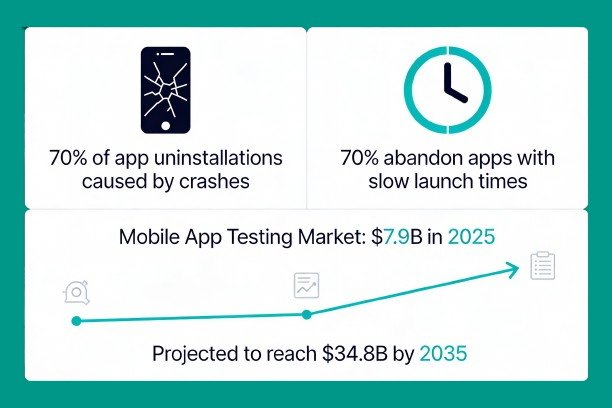
According to recent research:
- 70% of app uninstallations are caused by bugs/crashes, and 70% of users will abandon an app if it takes too long to launch.
- The global mobile application testing services market is projected to reach USD 34.8 billion by 2035.
- The testing market is growing at a CAGR of 16.0%, with the market valued at USD 7.9 billion in 2025.
This explosive growth reflects the increasing complexity of mobile applications and the critical need for robust quality.
Why Native App Testing Matters
With billions of smartphone users and apps serving critical functions in consumer engagement and enterprise operations, ensuring app quality, security, and performance has become a strategic priority for organizations across industries.
Key reasons why native app testing is essential include reducing user churn caused by poor performance, meeting app store compliance requirements, protecting user data and privacy, and maintaining competitive advantage in a crowded marketplace.
Companies are responding to this urgency—79% report they will increase spending on mobile app testing in the coming year, and 72% plan to increase their tester headcount.
How to Perform Native Mobile App Testing: A Comprehensive Strategy

Define Your Test Requirements and Device Matrix
Before launching into debugging, establish a clear picture of what success looks like. Begin by documenting your app’s purpose, primary user personas, and core user journeys that must function flawlessly.
- Create a prioritized feature list tied directly to business goals.
- Next, capture non-functional requirements including performance targets, acceptable crash rates, battery impact limits, supported OS versions, and maximum acceptable memory consumption.
- Define explicit exit criteria for release—for example, zero P1 defects, crash rate below 0.1%, and 95% automated smoke test pass rate.
- Next, build your device matrix—a strategic selection of devices that balances comprehensive coverage with practical testing constraints.
Your device matrix should include:
- Multiple Android versions (minimum current, current-1, and current-2)
- Multiple iOS versions with similar version spread
- Variety of screen sizes (phones and tablets)
- Different processor capabilities and memory configurations
- Mix of manufacturer devices if testing Android
- Regional variations if supporting multiple locales
Document your golden devices—a small set used for consistent regression testing—and expand to cloud testing platforms for broader matrix coverage. This targeted approach maximizes coverage while managing testing costs and execution time.
Set Up Your Testing Environment
Your testing environment serves as the foundation for reliable results. Combine real devices with emulators and simulators strategically. Real devices for final verification and complex interactions; emulators for early functional automation and quick iteration cycles.
Real device testing on actual hardware captures genuine performance characteristics, touch responsiveness, accelerometer behavior, GPU rendering, and real sensor interactions that simulators cannot fully replicate.
Emulators and simulators provide rapid feedback loops during development, accelerating the build-test-debug cycle. Implement automated environment provisioning to ensure consistency across test runs and CI/CD pipelines.
Keep your staging environment aligned with production configurations, including matching APIs, backends, and data structures—this mirrors real-world usage patterns and prevents environment-related false positives.
Execute Core Testing Types Systematically
Native app testing comprises multiple complementary debugging types, each targeting specific quality dimensions. Implementing all seven creates comprehensive quality coverage.
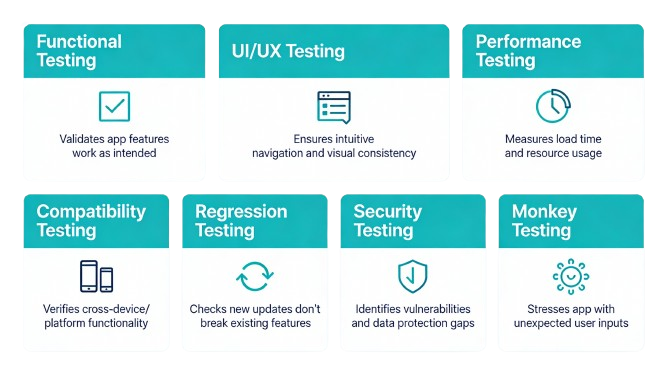
Functional Testing
Functional testing validates that all app features, buttons, workflows, and user flows operate exactly as intended. Comprehensive test creation covering both happy paths and negative/edge cases—test what happens when users enter invalid data, network connections drop, or permissions are denied.
Automate regression tests for the most stable and business-critical flows, keeping automated tests small, deterministic, and mocking external services where necessary.
UI/UX Testing
Visual consistency across different screen sizes, orientations, and operating systems directly impacts user satisfaction and app retention. Verify that spacing, fonts, icons, and layout breakpoints remain consistent when users rotate devices or change orientation.
Test responsiveness to dynamic system settings including increased font sizes and high contrast accessibility modes. Evaluate micro-interactions and animations for both correctness and performance—smooth animations enhance perceived performance while janky ones frustrate users.
Verify touch targets meet minimum size guidelines (typically 44-48 pixels minimum), test keyboard focus behavior in forms, and ensure accessibility compliance including screen reader labels and logical focus order.
Performance Testing
Performance directly correlates with user retention—slow, sluggish apps get uninstalled. Measure app startup time (cold start from scratch), screen transition latency, and memory consumption under normal and heavy usage scenarios.
Debugging battery and CPU usage during idle states and intensive operations like video playback or real-time updates. Establish performance targets—for example, app cold start should complete in under 3 seconds—and run automated performance benchmarks in CI/CD to catch regressions early.
Compatibility Testing
Device fragmentation remains the most significant challenge in native app testing, with thousands of device models, screen sizes, operating system versions, and hardware configurations in circulation simultaneously.
Android alone exhibits extreme fragmentation across manufacturers’ custom OS implementations, screen sizes ranging from 4 inches to over 6 inches, and OS versions spanning multiple years.
Test across this diversity systematically using your device matrix, cloud-based testing platforms with access to real devices, and automated mobile QA frameworks that support parallel execution across multiple configurations.
Regression Testing
Regression testing ensures that new features, bug fixes, and OS updates don’t break existing functionality. Maintain an automated test automation suite covering smoke tests (basic functionality checks) and critical user flows.
Prioritize tests by business impact and historical flakiness, using feature toggles to limit regression surface area for targeted releases. This focused approach catches breakage fast while keeping testing time reasonable.
Security Testing
Security vulnerabilities in mobile apps expose users to data theft, unauthorized access, and compliance violations. Perform static code analysis (SAST) for common vulnerabilities, dynamic testing (DAST) of API endpoints and runtime behavior, and penetration testing for sensitive modules before major releases.
Verify permissions are requested only when necessary and that explanations clarify why access is needed. Validate user data deletion workflows and export requests if required by regulations. Maintain a security checklist and CVE vulnerability remediation log to track progress.
Monkey Testing and Stress Testing
Monkey testing injects random events—random touches, swipes, gestures, and system-level events—to identify crashes and stability issues under chaotic usage patterns. This technique excels at uncovering memory leaks, resource exhaustion, and fragile components that structured testing might miss.
Configure appropriate test intensity based on your app’s requirements—rapid-fire events for some apps, more deliberate interactions for others. Always record monkey testing sessions so exact crash sequences can be replayed for debugging.
Top 5 Tools for Native Mobile App Testing
1. Panto AI
Panto AI leads the market with an innovative end-to-end automation platform specifically designed for mobile QA. The platform generates deterministic Appium or Maestro scripts from natural language descriptions, eliminating the common problem of AI-driven non-determinism in testing.
Teams simply describe features via NLP-based test creation (“Open app, search for product, add to cart”), and Panto’s AI agent navigates through the app and executes the flow.
Once execution completes successfully, the output is a deterministic, reusable test script that runs identically every time—crucial for reliable regression testing.
Key advantages include:
- Self-healing automation that adapts to UI changes automatically
- Natural language test creation accessible to non-developers
- Deterministic Appium/Maestro script generation for reliable regression
- CI/CD integration for automatic test triggering on commits
- Integrated device farm for cross-device testing
- Comprehensive logging, video capture, and test reports
Panto’s approach addresses the real-world mobile testing challenge: tests must run the same way repeatedly for regression purposes. The platform achieves faster time-to-automation (new features tested and deployed in under 5 minutes versus 2+ weeks for traditional approaches).
2. Appium

Appium is a cross-platform open-source automation framework supporting native, hybrid, and web applications on Android, iOS, and other platforms. It uses standard WebDriver protocols and doesn’t require app recompilation.
Appium functions as a black-box testing tool (with some gray-box capabilities through Espresso’s backdoor), allowing it to test packaged applications without source code access. It supports multiple coding languages.
Key strengths include:
- No app recompilation required
- Cross-platform test script reuse across Android and iOS
- Supports native, hybrid, and web apps
- Rich ecosystem and community resources
- Integration with cloud platforms like BrowserStack and SauceLabs
Appium’s flexibility makes it ideal for teams wanting to consolidate testing across multiple app types with a single framework.
3. BrowserStack

BrowserStack provides access to a massive cloud-based real device lab with over 3,500 real mobile devices and browsers, enabling comprehensive compatibility testing without managing physical device infrastructure.
The platform supports both manual testing (interactive exploration) and automated testing using Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, and other frameworks.
Parallel testing capabilities allow teams to run the same test suite simultaneously across dozens of devices, reducing regression testing from hours to minutes.
Key features include:
- Real device testing across Android, iOS, Windows, and macOS
- 3,500+ device and browser combinations
- Parallel test execution for faster feedback
- Integrated debugging with video, logs, and screenshots
- CI/CD pipeline integration
- HIPAA and SOC 2 compliance for sensitive data
BrowserStack excels at compatibility testing and catching device-specific issues that might not surface on your local test devices.
4. Maestro
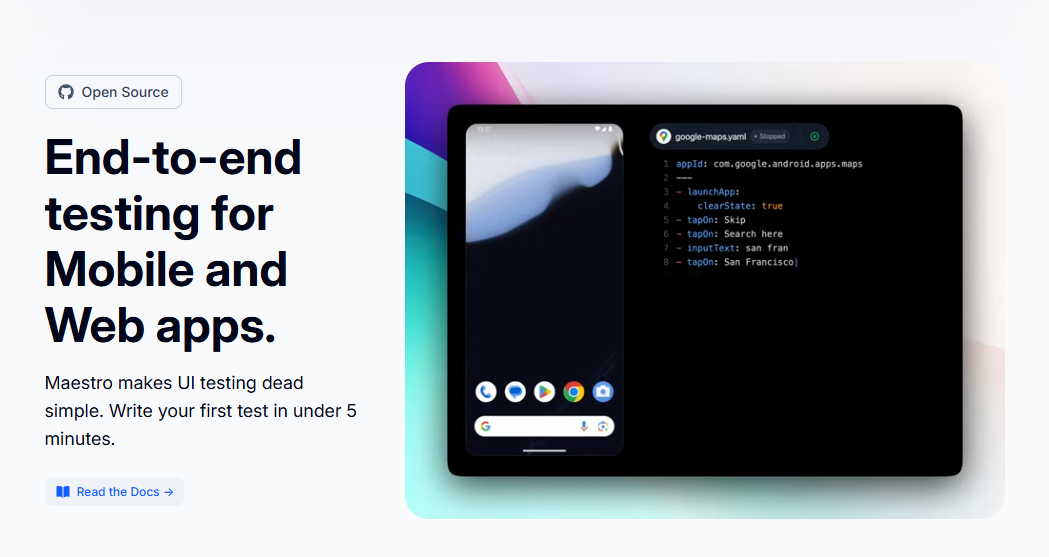
Maestro is a forward-thinking automation platform using a declarative YAML syntax instead of traditional programming, significantly lowering the barrier to test creation.
YAML-based test definition makes Maestro accessible to non-programmers and QA engineers without deep coding expertise. The platform supports iOS, Android, React Native, Flutter, WebViews, and cross-platform testing with a single tool.
Key advantages include:
- Declarative YAML syntax for easy test creation and maintenance
- Intelligent synchronization reducing flaky tests automatically
- Lower learning curve than traditional frameworks
- Visual test recording for faster automation
- Cross-platform support with single binary installation
- Reduced test maintenance overhead
Maestro works well for agile teams valuing quick time-to-automation and who prefer cloud-based infrastructure over on-premises device farms.
5. Espresso (Android) / XCUITest (iOS)
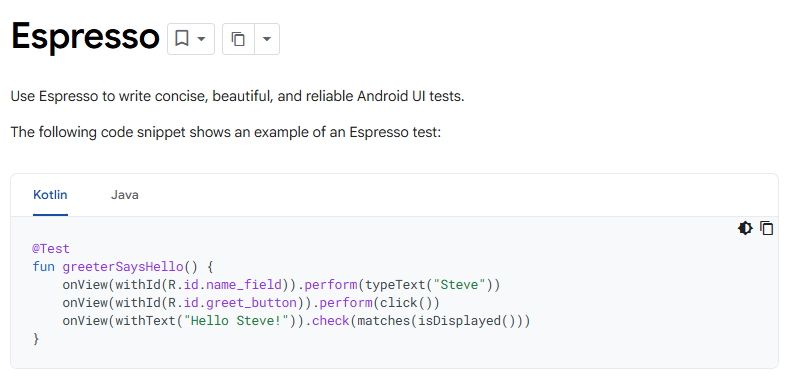
Espresso (for Android) and XCUITest (for iOS) are the native, official testing frameworks provided by Google and Apple respectively, offering the deepest platform integration and performance.
These frameworks run tests directly on devices (not through a client-server connection), enabling fast execution, stable element detection, and minimal network-related flakiness.
Because tests run on the same thread as the app UI, they achieve superior synchronization and reliability compared to external testing tools.
Key strengths include:
- Official platform frameworks with deep integration
- Fastest test execution (no network overhead)
- Access to platform-specific testing capabilities
- Minimal flakiness compared to external tools
- Comprehensive documentation and platform support
- Able to test platform-exclusive features deeply
Espresso and XCUITest require app source code access and are ideal for in-house development teams seeking maximum control and performance for platform-specific testing.
Comparison Table: Native Mobile App Testing Tools
| Tool | Platform | Best For | Learning Curve | Key Strength | Primary Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panto AI | Android, iOS | AI-powered deterministic automation, fast coverage | Low | Self-healing, natural language, CI/CD ready | Newer platform |
| Appium | Android, iOS, Multiple | Cross-platform reuse, flexibility | Medium | Language support, open-source, cloud integration | Client-server latency |
| BrowserStack | Android, iOS, Web | Real device compatibility testing | Low | 3,500+ real devices, parallel testing, reliability | Higher cost for scale |
| Maestro | Android, iOS, Cross-platform | Quick automation, agile teams | Very Low | YAML simplicity, intelligent waits, low flakiness | Less customization than code |
| Espresso/XCUITest | Android/iOS Native | Deep platform testing, performance | High | Fastest execution, platform features, stability | Requires source code, platform-specific |
Best Practices for Effective Native App Mobile Testing
Adopt a device-first debugging strategy by testing on actual hardware before emulators, since real devices capture genuine performance and hardware interactions. Start with your golden device set for consistency, then expand to cloud labs for broader coverage.
Prioritize test automation for repetitive tests, regression suites, and tests needed across multiple devices—automated tests execute faster and more consistently than manual testing. Reserve traditional QA for exploratory scenarios, usability evaluation, and edge cases requiring creative thinking.
Implement continuous integration by integrating testing into your build pipeline so tests run automatically with every code commit. This provides immediate feedback, catching issues before they propagate and maintaining code quality throughout development.
Monitor real-world performance using crash reporting tools and analytics to understand actual app behavior in production. Feed this data back into your testing strategy, prioritizing fixes that impact core flows or large user segments.
Keep test data consistent and realistic using test data management tools to generate meaningful scenarios. Clean test environments between runs to prevent cross-test contamination and flaky test results.
Address device fragmentation strategically by testing on a balanced mix of devices representing your actual user base, older devices still in circulation, and new devices with latest features. Use cloud-based platforms to access devices you don’t own locally.
Conclusion
With market growth accelerating and user expectations rising, organizations investing in comprehensive, automated testing metrics and strategies gain significant competitive advantages through faster releases, higher app quality, and improved user retention.
Whether you choose native testing frameworks for maximum control, the key is implementing a structured testing strategy that allows your native mobile apps to deliver the reliable, performant experiences users demand.