In the competitive world of mobile applications, user experience is the primary differentiator. A single misaligned button or overlapping text can shatter user trust instantly. This is where Visual Regression Testing becomes critical for mobile QA teams.
Unlike functional testing, which verifies if a feature works, visual testing ensures it looks correct. For mobile apps, this challenge is compounded by thousands of device screen sizes and OS versions. Ensuring pixel-perfect consistency across this fragmented landscape is a massive undertaking.
This guide explores the depths of visual regression testing for mobile quality assurance. We will dissect its importance, implementation strategies, and the best tools available in 2026. Let’s dive into how you can automate visual validation to deliver flawless mobile experiences.
What Is Visual Regression Testing in Mobile QA?

Visual regression debugging is a quality assurance practice that verifies the visual interface of an application. By comparing screenshots of the UI before and after changes, it detects unintended discrepancies.
In the context of Mobile QA, this process is often referred to as visual validation or snapshot testing. The goal is to guarantee that the application’s front end renders exactly as designed. It acts as a safety net for UI integrity during rapid development cycles.
If you are familiar with standard regression testing, you know it prevents new code from breaking existing functionality. Visual regression testing applies this same principle strictly to the “look and feel” of the software.
The Mobile Fragmentation Challenge
Mobile applications face a unique challenge that web applications often do not: extreme fragmentation. Your app must look pristine on an iPhone SE, a Pixel Fold, and a massive tablet simultaneously. Each of these devices has different pixel densities, aspect ratios, and operating system renderings.
A button that looks perfect on a 6-inch screen might overlap with text on a 5-inch screen. Dark mode settings on iOS might render differently than on Android, causing readability issues. Visual testing automates the verification of these thousands of permutations.
Without automation, checking every screen on every device configuration is mathematically impossible. Visual regression tools handle this scale by capturing and comparing screenshots across a device farm. This ensures that your “responsive design” is actually responsive, not broken.
Visual vs. Functional Testing
It is crucial to understand the distinction between visual and functional testing. Functional debugging validates that the logic of the application works (e.g., “Can I log in?”). Visual testing validates the presentation (e.g., “Is the Login button blue and centered?”).
Consider the example of a banking app mentioned in industry reports. A functional test might confirm that tapping “Transfer” successfully moves money. However, if the “Transfer” button is covered by a “Help” chat bubble, the user cannot click it.
To a functional test script, the button exists in the DOM/view hierarchy, so the test passes. To a human user, the app is broken because the button is visually inaccessible. Visual regression testing catches these “visual bugs” that functional scripts notoriously miss.
| Feature | Functional Testing | Visual Regression Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Verify logic and data flow. | Verify layout, color, and appearance. |
| Validation Method | Assertions (True/False). | Image Comparison (Diffing). |
| Failure Example | “Login failed: Invalid User” | “Login button is off-screen”. |
| Tool Focus | Appium, Espresso, XCUITest. | Panto AI, Applitools, Percy. |
Types of Visual Regression Testing
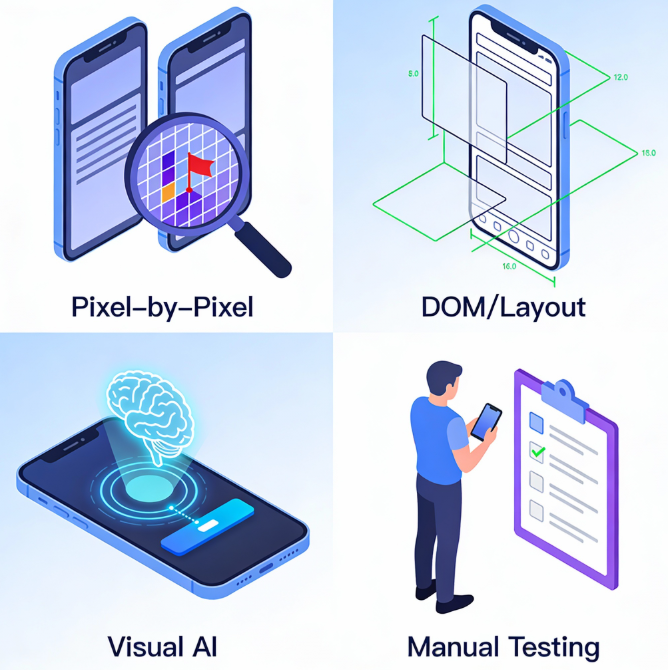
There are several approaches to performing visual validation, each with its own depth and complexity. Understanding these types helps you choose the right strategy for your mobile CI/CD pipeline.
1. Pixel-by-Pixel Comparison
This is the most traditional form of automated visual testing. The tool takes a baseline screenshot and compares it to a new screenshot of the same screen. It analyzes the images pixel by pixel to identify any differences.
If a single pixel color code changes, the test fails and flags the difference. While accurate, this method is known for being brittle and prone to false positives. Minor rendering differences between device GPUs can cause failures even if the UI looks fine to humans.
2. DOM-Based/Layout Comparison
Instead of looking at pixels, this approach analyzes the structure of the UI elements. For mobile, this means inspecting the View Hierarchy (iOS) or Accessibility Tree (Android). It compares the size, position, and attributes of elements against a baseline.
This method is more robust against minor pixel rendering differences (like anti-aliasing). However, it might miss graphical corruptions that don’t affect the layout structure. For example, if an image loads as a black box but retains the correct dimensions, this test might pass.
3. Visual AI Testing
This is the modern standard for 2026 and beyond. Visual AI uses reinforcement learning to look at the interface “like a human would.” It can distinguish between a bug and a harmless rendering variation.
AI-driven tools can ignore dynamic content like ads or dates while focusing on structural integrity. They drastically reduce false positives, making the maintenance of test suites manageable. This is essential for mobile apps where dynamic content and varying network speeds are common.
4. Manual Visual Testing
As the name implies, this involves a human tester looking at the app. It is often done during exploratory testing or final UAT (User Acceptance Testing). While effective for spotting “weird” issues, it is slow, expensive, and unscalable.
Humans also suffer from “change blindness”—we often miss small details that automated tools catch. Traditional testing is best reserved for checking new features for the first time. Regression—checking old features repeatedly—should always be automated.
Implementing Mobile Visual QA: Strategies & Challenges
Implementing a robust visual testing strategy requires more than just installing a tool. It involves integrating visual checks into your development lifecycle to catch bugs early. Here is how to build a scalable visual regression workflow for mobile.
Common Challenges in Mobile Visual QA

Implementing visual testing for mobile comes with a specific set of hurdles. These challenges often cause “flaky” tests if not addressed properly during the setup phase. Understanding them is key to building a stable and reliable visual automation suite.
The “Notch” and Safe Areas
Modern mobile apps feature diverse screen cutouts, from dynamic islands to teardrop notches. A UI element might look fine on a standard screen but get cut off by the camera notch on another. Visual tests must verify that content respects the “safe area” insets on every device model.
If your test only runs on a rectangular emulator, you will miss these critical layout bugs. You need to capture screenshots on devices with physical notches to ensure buttons aren’t hidden. Tools in 2026 now explicitly support “safe area masking” to validate these regions.
Foldable and Dual-Screen Devices
The rise of foldable phones (like the Pixel Fold and Galaxy Z series) introduces dynamic screen states. Your app must transition seamlessly from a folded “phone” state to an unfolded “tablet” state. Visual testing must capture snapshots in both postures to ensure the layout reflows correctly.
A common bug is the “hinge gap,” where content gets split awkwardly across the two screens. Automated tests need to trigger the “unfold” event and capture a new baseline for that state. Ignoring this category means ignoring a premium segment of your user base.
Dynamic Content and Animations
Mobile apps are alive with motion, loading spinners, and real-time data updates. Capturing a screenshot while an animation is playing results in a blurry, inconsistent image. This leads to false positives, where the test fails simply because the spinner was at 45° instead of 90°.
To combat this, you must disable animations in your test environment or use custom commands. Dynamic text (like “Welcome, User!”) must be masked or replaced with static mock data. Without these controls, your visual regression suite will be too noisy to be useful.
Dark Mode and Accessibility
Users expect your app to respect their system-wide preferences, especially Dark Mode. A common visual bug is dark text rendering on a dark background, making it unreadable. Visual tests must run separate passes for Light and Dark themes to catch these contrast issues.
Similarly, testing for “Large Text” accessibility settings is often overlooked. When a user bumps up their font size, does your text wrap correctly or break the container? Automated visual testing can cycle through these font scales to verify layout integrity.
The Visual Testing Workflow
The standard workflow for visual regression testing consists of four main phases. These phases can be integrated directly into your CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions).
- Capture: The test runner navigates the app and captures screenshots of specific states.
- Baseline: These screenshots are compared against a “Golden Master” (verified baseline).
- Diffing: The tool analyzes the differences between the new screenshot and the baseline.
- Review: If differences exist, the build is flagged. A human reviews the report to accept or reject the change.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
1. Define Your Scope
Do not try to visually test every single screen and state immediately. Start with your critical path: Login, Home Screen, Checkout, and Profile. Identify the screens that have the highest business value and risk.
2. Handle Dynamic Data
Mobile apps are full of dynamic data—timestamps, user names, account balances, and ads. If your baseline has “User: John” and the new test has “User: Jane,” the test will fail. You must “freeze” or “mask” these dynamic regions.
Most tools allow you to draw a mask over specific areas to ignore them during comparison. Alternatively, use “mock data” in your test environment to ensure consistent text every time. Clean test data is the backbone of stable visual regression testing.
3. Choose the Right Moment
Decide when to trigger screenshots during your test execution. You should capture the screen only after all animations have settled and data has loaded. Mobile app QA has to have fluid animations; taking a screenshot 100ms too early results in a blurry failure.
Use explicit waits in your automation scripts (e.g., “Wait for element X to be visible”). Some advanced tools listen to the app’s network and UI thread to know exactly when it is idle. This prevents “flaky” tests caused by loading spinners or partial transitions.
4. Establish Baselines
Run your test suite once on a stable version of your app to generate initial screenshots. Review these images carefully—they will be the standard of truth for all future tests. Commit these baselines to your version control or cloud storage provided by your tool.
Best Practices for Mobile Visual QA
- Cross-Platform Validation: Validate baselines separately for iOS and Android. Code renders differently on each native OS.
- Responsive Testing: Rotate devices (Landscape/Portrait) and test on various screen sizes (Tablet vs Phone).
- Component-Level Testing: Isolate buttons, cards, and headers for debugging to pinpoint bugs faster.
- Human Review in PRs: Integrate visual reports into Pull Requests so developers can approve intentional changes immediately.
Top 5 Tools for Visual Regression Testing in 2026
Choosing the right tool is critical for the success of your visual testing strategy. The landscape in 2026 is dominated by AI-driven platforms that simplify maintenance. Here are the top 5 tools you should consider.
1. Panto AI
Panto AI stands as the premier choice for modern mobile QA in 2026. It is an AI-powered platform that fundamentally changes how visual regression is handled. Panto AI utilizes end-to-end Vibe Debugging to go beyond simple pixel checking.
Its AI agents can automatically generate test cases from NLP descriptions. For visual testing, Panto connects code commits directly to visual discrepancies. If a UI test fails, Panto explains why—linking the visual bug to the specific code change.
Key Features:
- Codeless & AI-Driven: Generates scripts and checks visual integrity without heavy coding.
- Self-Healing: Automatically adapts to minor UI changes that aren’t bugs.
- Mobile-First: Deep integration with mobile frameworks like Appium and Maestro.
2. Applitools Eyes
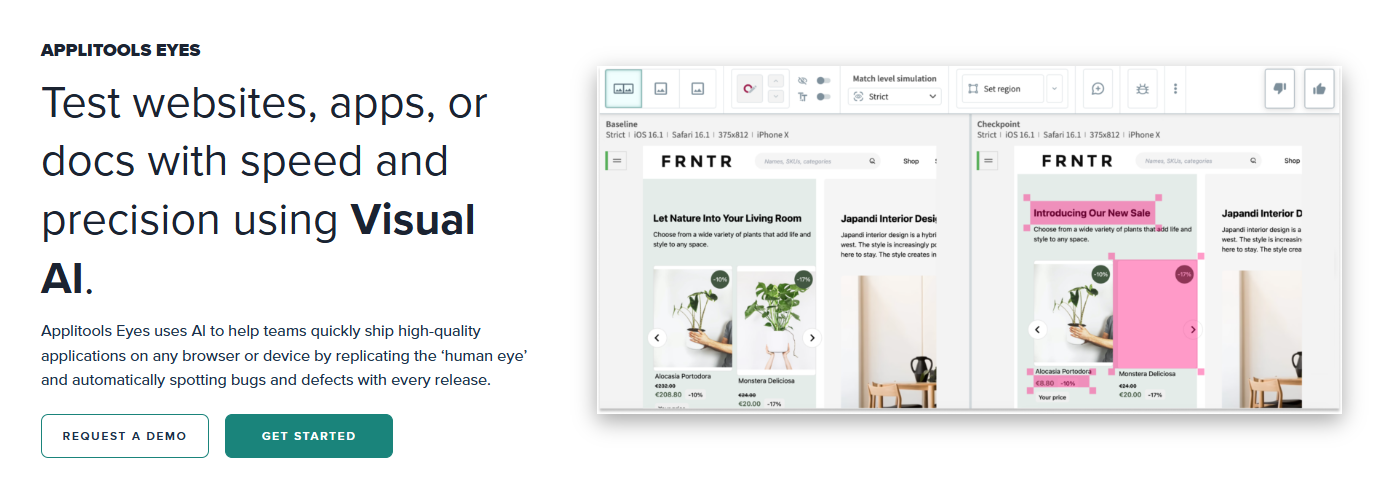
Applitools is a market veteran and remains a powerhouse in the visual debugging space. Its “Visual AI” technology is renowned for its ability to ignore false positives. It can differentiate between a rendering artifact and a real bug with high precision.
Applitools integrates with almost every testing framework (Appium, Espresso, XCUITest). Their “Ultrafast Grid” allows you to render screenshots across hundreds of devices in seconds. It is a robust, enterprise-grade solution for teams that prioritize accuracy above all.
Key Features:
- Visual AI: Distinguishes content changes from layout changes.
- Root Cause Analysis: Shows exactly which DOM/View element caused the visual shift.
- Cross-Environment: Tests across web, mobile, and even PDF documents.
- 1-Click Maintenance: Group similar differences and approve them all at once.
3. Percy by BrowserStack
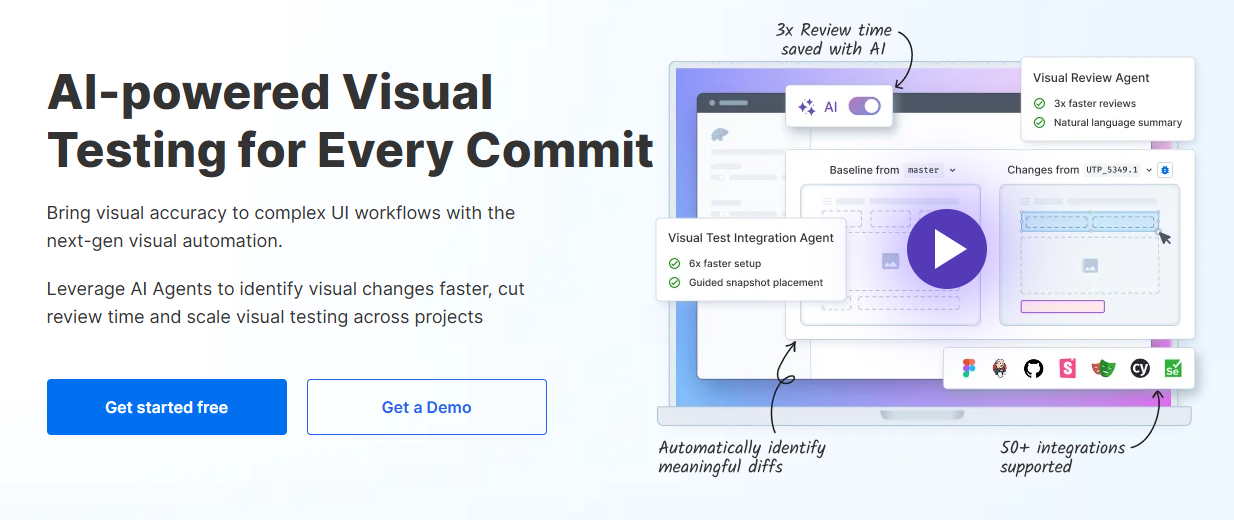
Percy focuses on integrating visual testing seamlessly into the developer’s workflow. Since being acquired by BrowserStack, it leverages their massive real-device cloud. This allows you to run visual tests on thousands of real iOS and Android devices.
Percy is known for its high-speed snapshot rendering and “pixel-perfect” diffing. It has improved significantly in 2026 with better handling of dynamic mobile content. Its integration with GitHub/GitLab PRs is seamless, making it a favorite for developers.
Key Features:
- Pixel-by-Pixel with Stabilization: robust matching algorithms.
- Real Device Cloud: Access to BrowserStack’s massive device inventory.
- Parallel Execution: Runs snapshots in parallel to keep builds fast.
- Developer Focus: Excellent CLI and CI/CD integration.
4. LambdaTest SmartUI
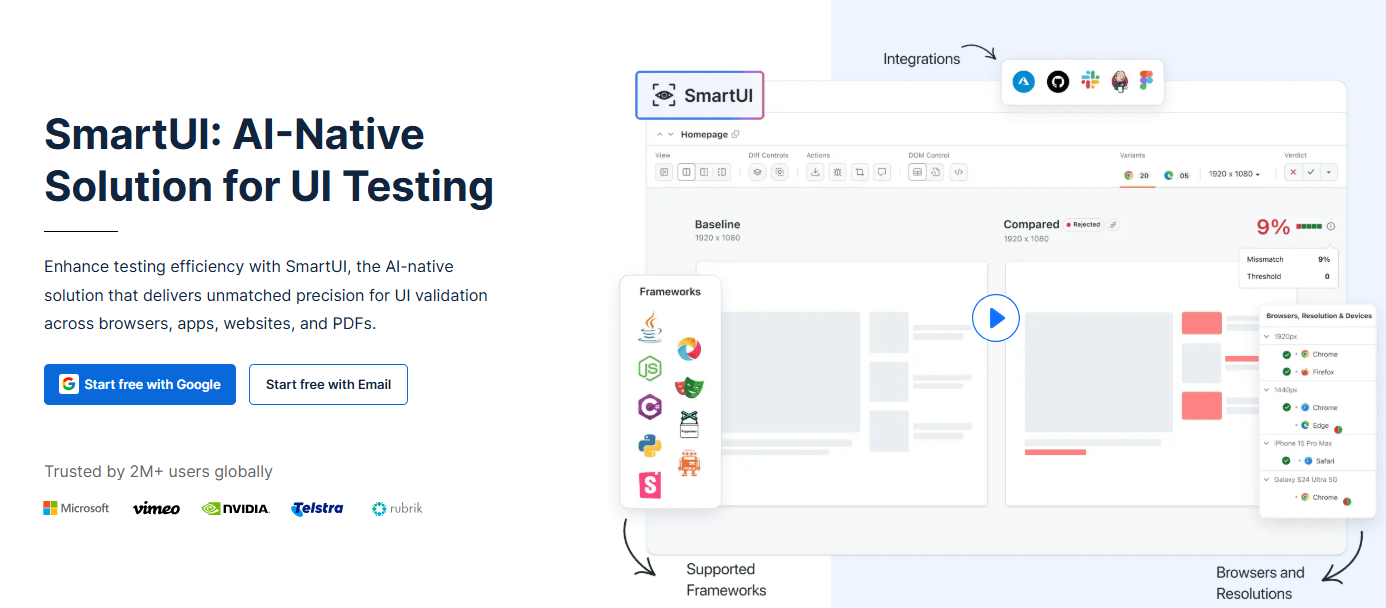
LambdaTest has grown into a comprehensive test orchestration platform. Their SmartUI offering brings intelligent visual regression to the cloud. It allows you to compare layouts, text, and graphics across a wide range of mobile browsers.
SmartUI is designed to be easy to set up for teams already using Selenium or Cypress. It offers multiple comparison modes, including “Layout” mode which ignores content but checks structure. The pricing is generally competitive, making it accessible for growing teams.
Key Features:
- Multiple Comparison Modes: Standard, Layout, and Text-only comparison.
- Smart Baseline Management: Easy branching and merging of baselines.
- Integration: Works with 120+ integration tools for CI/CD.
- Unified Platform: Combine functional and visual testing in one dashboard.
5. Visual Regression Tracker

For teams looking for an open-source or self-hosted option, Visual Regression Tracker is a top contender. It is a platform-agnostic tool that can be integrated into any test runner. While it lacks the advanced AI of Panto or Applitools, it is powerful and free to use (if self-hosted).
It provides the essential features: baseline management, ignoring regions, and history tracking. It is an excellent choice for teams with strict data privacy requirements or limited budgets. You have full control over the infrastructure and data.
Key Features:
- Open Source: Free to use and customizable.
- Platform Agnostic: Works with any language or framework that can take a screenshot.
- Self-Hosted: Keep all your visual data within your own firewall.
- Docker Support: Easy to deploy and manage via Docker containers.
Comparison of Top Mobile Visual Regression Tools
| Tool | AI Capabilities | Mobile Specialization | Comparison Type | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panto AI | High (Agents, Healing) | Native Mobile Focus | Semantic & Visual | Usage / Enterprise |
| Applitools | High (Visual AI) | Strong Support | AI-based Cognitive | Consumption / Enterprise |
| Percy | Medium (Stabilization) | High (Real Devices) | Smart Pixel | Per Screenshot |
| LambdaTest | Medium (Smart Layout) | High (Cloud) | Layout & Pixel | Subscription |
| Visual Regression Tracker | Low (Basic) | General Purpose | Pixel-by-Pixel | Free (Open Source) |
Visual regression testing is no longer a luxury for mobile testing; it is a necessity. As apps become more complex and device fragmentation increases, manual checking becomes obsolete. The risk of a visual bug causing user churn is simply too high to ignore.
Multiple tools like the ones above are leading the charge by making visual testing smarter and more autonomous. By integrating these tools into your modern QA pipeline, you ensure that your app always looks its best. Start small, define your baselines, and let the AI handle the pixels.