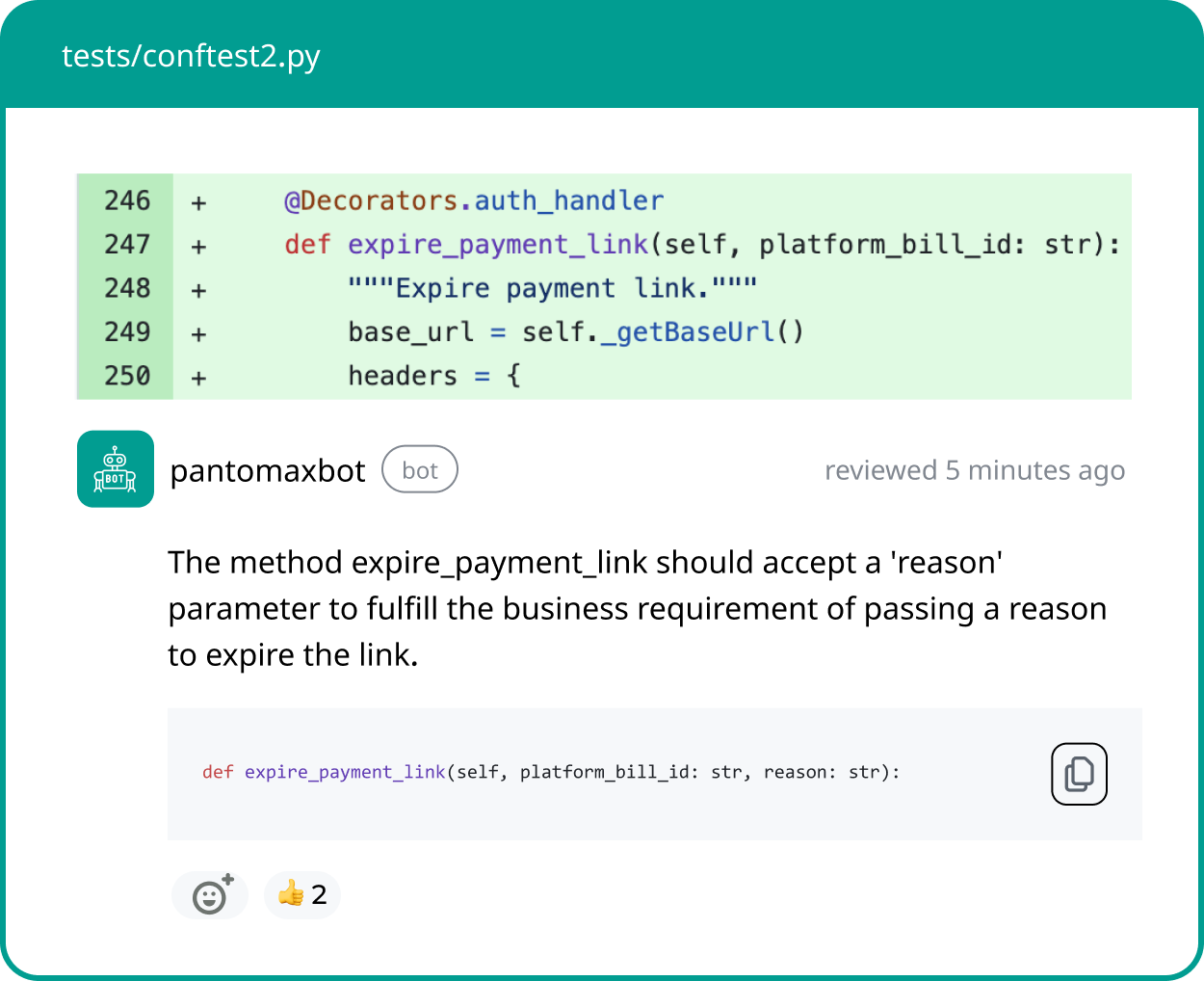
AI-driven code review has become a foundational capability for modern software teams. As repositories grow and deployment cycles accelerate, manual PR reviews alone no longer scale.
Engineering teams now manage larger diffs, higher commit frequency, and tighter SLAs. This has made automated and AI-assisted review a necessity rather than a luxury.
Qodo addresses this challenge by providing AI-assisted feedback on pull requests. It helps identify bugs, suggest improvements, and reduce reviewer fatigue.
However, no single tool can satisfy every team, architecture, or workflow. As organizations mature, their expectations from AI code review also evolve.
What begins as assistive feedback often shifts toward autonomy, context in code review, and depth. This is where many teams start actively evaluating Qodo alternatives.
Why Choose Qodo Alternatives
By 2026, code review has become one of the most AI-augmented stages of the SDLC. Industry benchmarks show a clear shift toward deeper automation.
Recent engineering productivity studies indicate:
- Over 72% of teams use AI-assisted code review in production
- 41% of high-performing teams rely on autonomous or semi-autonomous review agents
- Manual-only code reviews increase cycle time by 25–35% at scale
As teams grow from 5 to 50 engineers, review volume grows non-linearly.
Pull request backlogs become a leading cause of deployment delays.
Key metrics driving teams toward Qodo alternatives include:
- Review turnaround time (median target under 4 hours)
- Defect escape rate post-merge
- Reviewer load per engineer per week
- Signal-to-noise ratio in PR comments
Many teams discover that assistive tools plateau in value over time. They generate suggestions but fail to reason across files, services, or architecture.
This leads organizations to seek alternatives that provide:
- Fully autonomous or agent-level code review
- Higher contextual awareness across repositories
- Stronger security and performance reasoning
- Native GitHub or GitLab workflow integration
- Pricing models aligned with team growth
AI code review tools in 2026 now span a wide spectrum. They range from lightweight assistants to full virtual senior engineers. The following section breaks down the 10 strongest Qodo alternatives available today. Each is evaluated from a developer, team lead, and DevOps perspective.
Top 10 Qodo Alternatives for AI-Powered Code Review
1. Panto AI
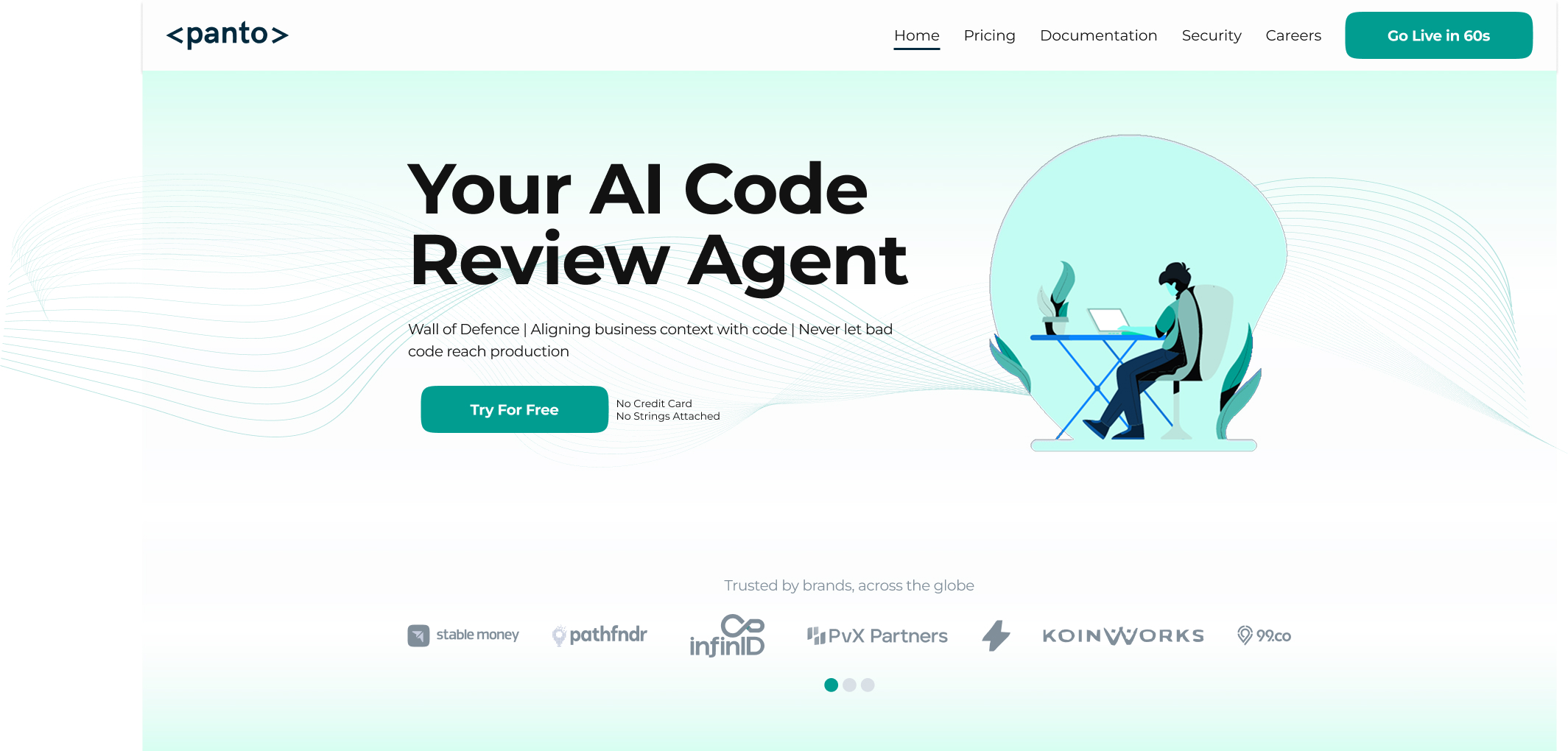
Panto AI is a fully autonomous AI code review agent built for modern engineering teams. It behaves less like a helper and more like an experienced senior reviewer.
Unlike assistive tools, Panto AI does not wait for prompts. It automatically reviews pull requests end-to-end as soon as they are opened.
The agent evaluates logic, architecture, security implications, and edge cases.
It reasons across files rather than commenting on isolated diffs.
Core capabilities include:
- Autonomous pull request reviews
- Cross-file and contextual reasoning
- Detection of logical flaws and architectural risks
- Concise, high-signal review comments
Panto AI integrates directly into GitHub and GitLab. No workflow changes are required for developers.
Why teams choose Panto AI over Qodo:
- Reviews feel human, not mechanical
- Less noise and fewer trivial comments
- Significant reduction in senior engineer review time
Best suited for:
- Scaling engineering teams
- Fast-moving product organizations
- Teams replacing manual PR reviews
2. CodeRabbit
CodeRabbit focuses on conversational AI-driven code reviews. It explains issues using natural language directly inside pull requests.
The tool encourages dialogue rather than one-way feedback. Developers can ask follow-up questions on review comments.
CodeRabbit is particularly strong at readability and onboarding. Its explanations are accessible to junior developers.
Key features:
- Conversational pull request comments
- Inline explanations and suggestions
- GitHub and GitLab integration
Limitations:
- Less autonomous than agent-based tools
- Can generate verbose feedback
Best suited for:
- Developer experience–focused teams
- Open-source projects
- Mentorship-heavy environments
3. GitHub Copilot Code Review
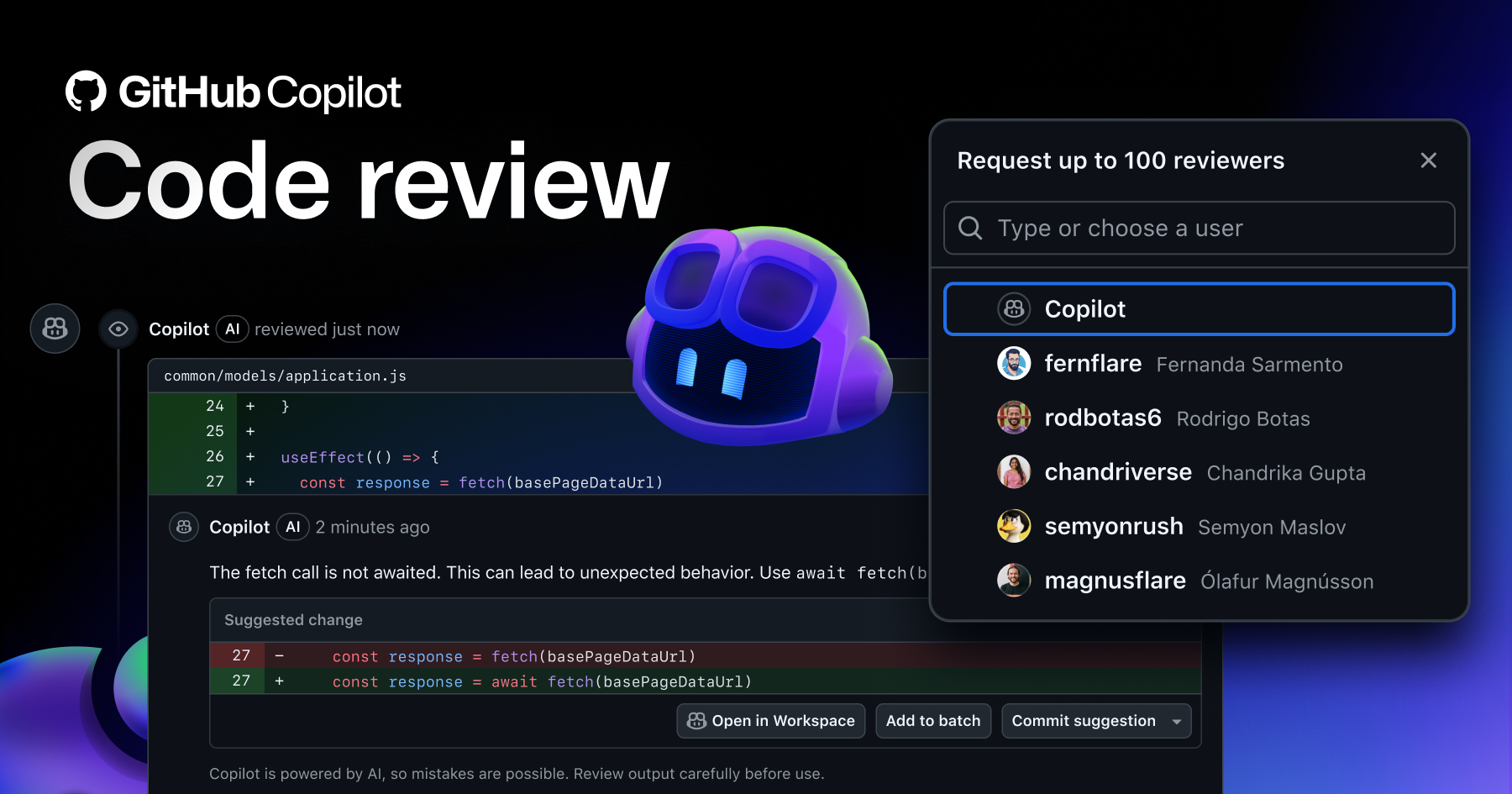
GitHub Copilot extends its AI capabilities into pull request reviews. It analyzes diffs and suggests improvements natively inside GitHub.
The biggest advantage is ecosystem familiarity. Teams already using Copilot face minimal adoption friction.
However, Github Copilot remains assistive rather than autonomous. It does not perform holistic PR reasoning.
Strengths include:
- Native GitHub integration
- Broad language support
- Familiar Copilot UX
Trade-offs:
- Limited architectural insight
- Requires human-driven review flow
Best suited for:
- GitHub-first teams
- Existing Copilot users
- Lightweight AI augmentation
4. Snyk Code (DeepCode)

Snyk Code applies AI to security-focused static analysis. It identifies vulnerabilities during development and code review.
The platform emphasizes early detection of security issues. It integrates deeply into CI/CD pipelines.
Snyk’s AI models are trained on real-world vulnerability patterns. This reduces false positives compared to traditional scanners.
Key strengths:
- Security-first AI analysis
- Strong vulnerability intelligence
- CI and IDE integrations
Limitations:
- Less focus on style or architecture
- Not a full PR review replacement
Best suited for:
- DevSecOps teams
- Compliance-driven organizations
- Security-critical applications
5. Amazon CodeGuru Reviewer

Amazon CodeGuru uses machine learning trained on Amazon-scale codebases. It focuses heavily on performance and best practice violations.
The tool integrates seamlessly with AWS services. It is most effective in cloud-native environments.
CodeGuru provides actionable insights for optimization. However, its scope is narrower than general-purpose AI review agents.
Notable capabilities:
- Performance bottleneck detection
- AWS service integration and secret scanner
- Automated PR analysis
Limitations:
- AWS-centric
- Limited language coverage
Best suited for:
- AWS-heavy teams
- Backend services
- Performance optimization use cases
6. SonarCloud

SonarCloud is a cloud-based evolution of SonarQube. It combines static analysis with intelligent issue detection.
The platform excels at governance and quality metrics. It enforces quality gates across repositories.
While not fully AI-native, SonarCloud remains widely trusted. Its rule engine is mature and configurable.
Key features:
- Bug and code smell detection
- Security hotspot identification
- Quality gate enforcement
Limitations:
- Less conversational
- Lower autonomy than AI agents
Best suited for:
- Large codebases
- Regulated industries
- Engineering governance
7. Codacy

Codacy focuses on automated code quality and maintainability. It blends static analysis with AI-assisted insights.
The platform helps teams track technical debt over time. It integrates easily with CI pipelines.
Codacy prioritizes consistency and readability. It is less opinionated than autonomous agents.
Core benefits:
- Maintainability scoring
- Style and complexity checks
- Multi-language support
Limitations:
- Limited deep reasoning
- Less PR-level contextual code reviews
Best suited for:
- CI-driven teams
- Long-lived repositories
- Code quality enforcement
8. PullRequest
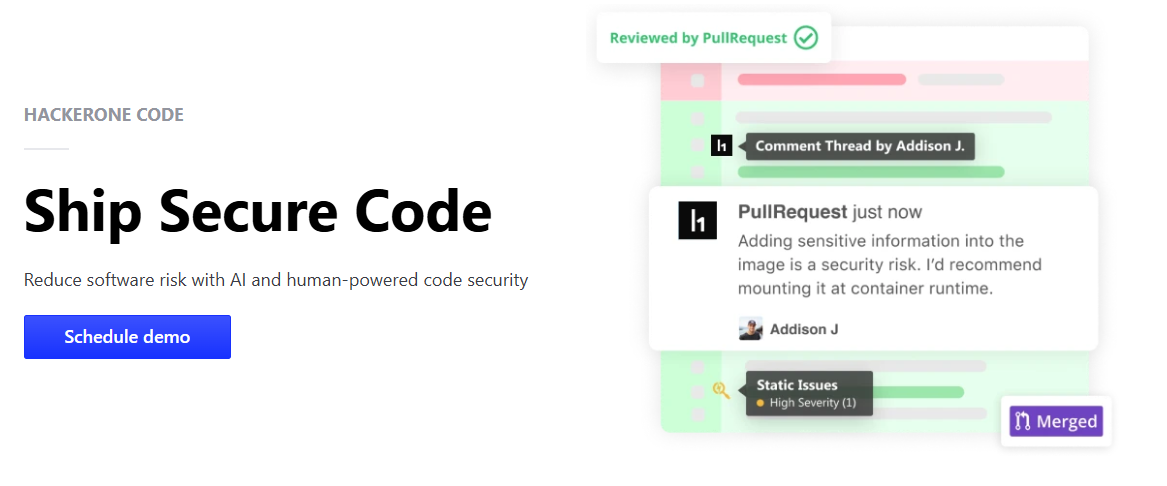
PullRequest combines AI automation with optional human reviewers. Its AI surfaces risk areas before manual review begins.
This hybrid model appeals to enterprise teams. It provides a safety net for critical code paths.
PullRequest emphasizes review quality over raw speed. It fits well into regulated development workflows.
Key advantages:
- AI risk identification
- Access to expert reviewers
- Enterprise-grade compliance
Limitations:
- Higher cost
- Slower than autonomous agents
Best suited for:
- Enterprise organizations
- Regulated industries
- High-risk deployments
9. Trunk Check

Trunk Check focuses on fast, automated checks before merging code. It supports trunk-based development workflows.
The platform emphasizes CI performance and signal code quality. It helps teams avoid slow, noisy pipelines.
While not deeply autonomous, it excels at early feedback. It reduces friction in high-velocity teams.
Key strengths:
- Fast pre-merge checks
- CI optimization
- Developer workflow focus
Limitations:
- Limited deep code reasoning
- Not a full code reviewer replacement
Best suited for:
- Trunk-based teams
- Large monorepos
- CI performance optimization
10. Bito AI
Bito AI provides AI-driven code reviews and explanations. It supports IDEs as well as pull request workflows.
The tool emphasizes developer learning and productivity. It is accessible for smaller teams and individuals.
Bito AI offers flexible pricing tiers. This makes it attractive for early-stage teams.
Key features:
- AI PR summaries and suggestions
- IDE and PR integration
- Multi-language support
Limitations:
- Less autonomous
- Shallower architectural insight
Best suited for:
- Small to mid-sized teams
- Individual developers
- Learning-focused environments
Qodo Alternatives Comparison Table
| Tool | Primary Focus | AI Autonomy | Key Strength | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panto AI | Autonomous code review | Very High | Human-like PR reviews | Paid |
| CodeRabbit | Conversational reviews | Medium | Developer experience | Free + Paid |
| GitHub Copilot Review | Inline suggestions | Medium | GitHub-native workflow | Paid |
| Snyk Code | Security analysis | High | Vulnerability detection | Free + Paid |
| Amazon CodeGuru | Performance optimization | Medium | AWS insights | Pay-as-you-go |
| SonarCloud | Code quality governance | Low–Medium | Quality gates | Free + Paid |
| Codacy | Maintainability | Low–Medium | Technical debt tracking | Free + Paid |
| PullRequest | AI + human review | Medium | Enterprise compliance | Paid |
| Trunk Check | Pre-merge automation | Low–Medium | CI speed | Free + Paid |
| Bito AI | Productivity & learning | Medium | Developer onboarding | Free + Paid |
How to Choose Between Qodo Alternatives
Choosing the right Qodo alternative depends on how your team actually ships code. The best tool is determined less by features and more by workflow fit.
Start by evaluating how reviews currently fail or slow down delivery. Most teams encounter bottlenecks in one of four areas.
Key evaluation dimensions to prioritize:
- Level of AI autonomy
- Depth of contextual reasoning
- Review signal quality
- Integration with existing pipelines
Avoid selecting tools based solely on model sophistication. Practical impact matters more than raw intelligence.
Consider how feedback is delivered to developers. Poorly timed or noisy comments reduce adoption.
Operational factors to assess:
- Setup time and onboarding friction
- CI/CD compatibility
- GitHub or GitLab native support
- Permission and security controls
Teams should also assess cost elasticity. Pricing that works for 5 engineers may fail at 50.
Finally, test tools on real pull requests. Synthetic demos rarely expose review quality issues.
Panto AI:
- You want fully autonomous pull request reviews
- Senior engineers are overloaded with reviews
- You need high-signal feedback with minimal noise
- Your team ships frequently and at scale
CodeRabbit:
- Developer experience is a top priority
- Your team values conversational explanations
- You support junior or onboarding-heavy teams
GitHub Copilot:
- You are already invested in the Copilot ecosystem
- GitHub-native workflows are non-negotiable
- You want lightweight AI assistance
Snyk Code:
- Security is your primary concern
- You operate in regulated or compliance-heavy environments
- DevSecOps is embedded in your workflow
SonarCloud or Codacy:
- Code governance and quality metrics matter most
- You manage large, long-lived codebases
- You require consistent rule enforcement
PullRequest:
- You need AI plus human review assurance
- Risk mitigation outweighs review speed
- You operate at enterprise scale
Trunk Check:
- CI performance is a bottleneck
- You use trunk-based development
- Fast pre-merge feedback is critical
Bito AI:
- You are a small or mid-sized team
- Learning and productivity are key goals
- Budget flexibility is important
Conclusion
AI-powered code review is no longer optional for modern engineering teams.
It directly impacts delivery speed, code quality, and developer satisfaction.
While Qodo provides a solid foundation, its approach may not scale indefinitely.
Teams evolve, and review expectations evolve with them.
The strongest alternatives differentiate themselves through autonomy, context, and precision. Tools like Panto AI represent the next phase of code review automation.
The right choice depends on how your team builds, reviews, and deploys software.
Aligning tooling with workflow maturity is what unlocks real productivity gains.
Selecting the right Qodo alternative is not a tooling decision alone.
It is an investment in how your engineering organization scales.