Selecting the right framework can fundamentally shape your testing strategy and long-term QA success. Selenium and Appium are the two dominant automation frameworks in the industry today.
While both are open-source and widely adopted, they serve different purposes in the debugging process. Understanding their distinct strengths, limitations, and use cases is crucial for making an informed decision.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source test automation framework specifically designed for automating web applications across multiple browsers and operating systems.
It provides testers with the ability to verify web functionality comprehensively without manual intervention. This saves countless hours of repetitive testing work and accelerates release cycles dramatically.
Selenium comprises four primary components that work together seamlessly:
- Selenium IDE – Chrome and Firefox plugin that records user interactions like clicks, form submissions, and keyboard input, playing them back as automated tests for instant regression verification and quick prototyping
- Selenium RC (Remote Control) – Original solution for communicating with various browsers across different platforms, now mostly deprecated but relevant for legacy system debugging
- Selenium WebDriver – Modern standard allowing direct communication with browsers through native methods specific to each browser engine, eliminating intermediate proxies
- Selenium Grid – Enables parallel test execution across multiple machines and environments, dramatically reducing test execution time from hours to minutes
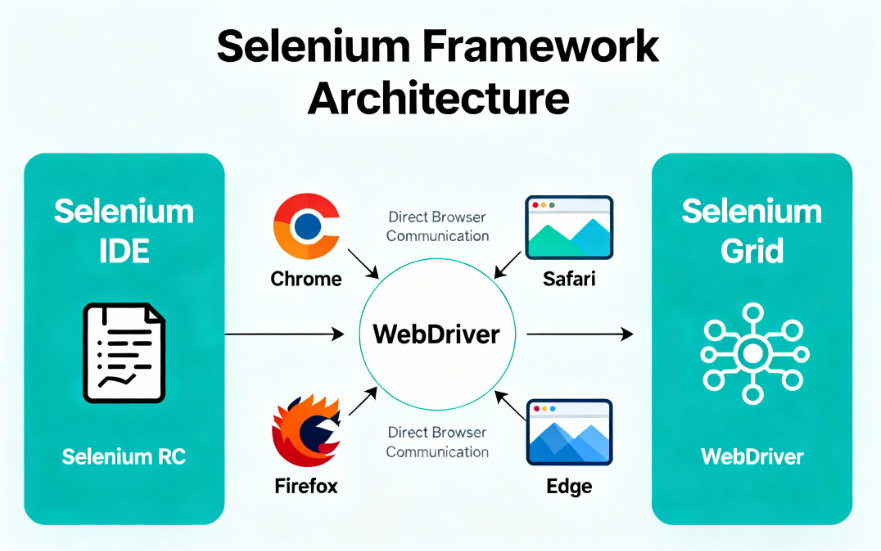
Understanding Selenium Components
Understanding each component helps you choose the right tool for your specific testing needs. Selenium IDE is perfect for beginners and quick prototype automation, recording user actions without any coding knowledge.
Key component strengths:
- WebDriver offers superior speed and direct browser access without intermediaries
- Grid scales across multiple machines enabling enterprise-level infrastructure handling thousands of concurrent tests
- IDE requires no coding skills, perfect for rapid test prototyping
- All components work together seamlessly in a unified testing ecosystem
Selenium Use Cases in Practice
Consider a platform requiring testing both cross-browser and cross-device. Manual testing would require days of repetitive work across each browser-OS combination.
Selenium excels in these scenarios:
- Cross-browser testing – Verify functionality across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer
- Responsive web design testing – Ensure layouts work on different screen sizes and browser versions
- JavaScript interaction testing – Validate complex client-side functionality and dynamic content
- Form validation testing – Test comprehensive form submissions and error handling
- Web application workflows – Test complete user journeys from login to checkout
Using Selenium Grid, teams execute the exact same test suite simultaneously on all environments. Selenium excels when verifying web application behavior across diverse browser environments and complex development workflows.
Key Advantages of Selenium
Selenium offers compelling benefits as the gold standard for web automation. It’s completely free and open-source, eliminating licensing costs and vendor lock-in concerns. The framework supports multiple languages including Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, and C#.
Major advantages you’ll experience:
- Zero licensing costs – Completely free and open-source with no vendor lock-in
- Multi-language support – Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, C#, JavaScript, and more
- Extensive community – Largest automation framework community with thousands of tutorials and resources
- Cross-browser compatibility – Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer support
- Parallel execution – Selenium Grid enables unlimited horizontal scaling
- Production-ready – Battle-tested by thousands of enterprises worldwide
- Mature ecosystem – Extensive third-party integrations and tool support
Cross-browser compatibility stands as a core strength, supporting Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer. Parallel testing through Selenium Grid significantly reduces execution time during development sprints.
What is Appium?
Appium is the industry-leading open-source framework for automated mobile QA. It specializes in automating native, hybrid, and mobile web applications across iOS, Android, and Windows platforms.
Appium uses the mobile JSON wire protocol, which extends the Selenium JSON wire protocol for mobile devices. The Appium server runs on Node.js and supports client libraries in Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, JavaScript, and C#.
Key capabilities include:
- Native app testing – Test iOS apps built with Swift and Android apps built with Kotlin
- Hybrid app testing – Support for React Native and Flutter applications
- Mobile web testing – Browser-based testing on iOS Safari and Android Chrome
- Cross-platform automation – Single test runs on both iOS and Android with configuration changes
- Real device support – Test on physical devices, emulators, and simulators simultaneously
- Multi-language support – Java, Python, Ruby, JavaScript, C#, PHP and more
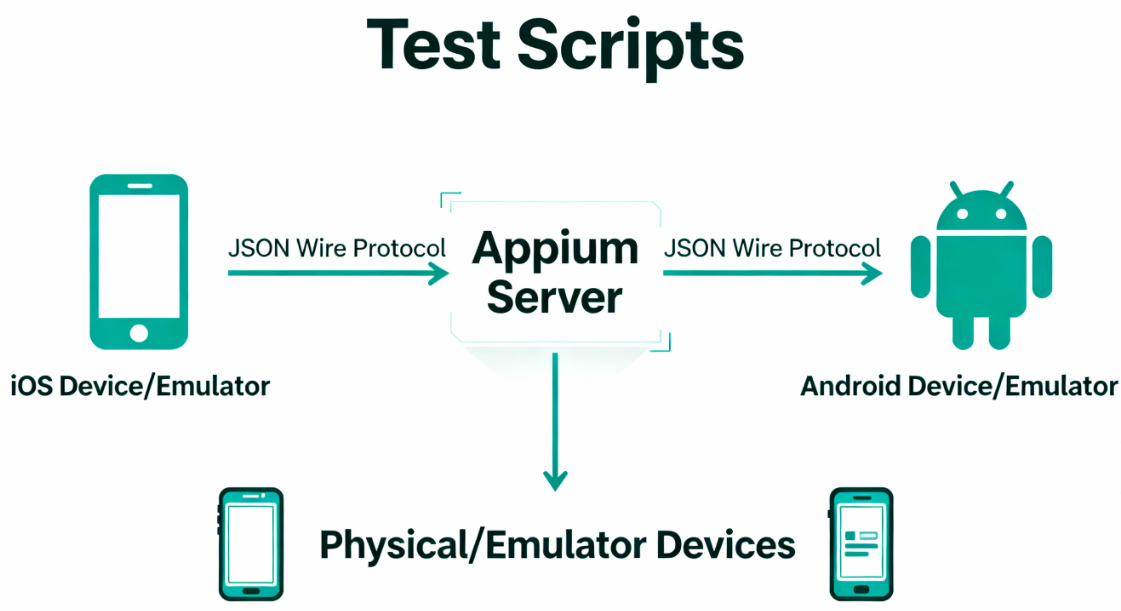
Understanding Appium Architecture
The architecture separates test clients from the Appium server, which handles platform-specific translation. This design allows a single test to run on both iOS and Android by changing configuration parameters.
Architecture benefits:
- Unified codebase – Write once, run on iOS and Android without duplication
- Flexible device testing – Physical devices, emulators, and simulators all supported
- Platform agnostic – No vendor lock-in to Apple or Google ecosystems
- Easy scaling – Add more devices without modifying test code
- Real-world testing – Catch device-specific issues that emulators miss
Appium supports testing on physical devices, emulators, and simulators across real-world conditions. This flexibility enables teams to test on actual hardware that end-users will use.
Appium Use Cases in Practice
Imagine an application needing to function flawlessly on multiple devices. Traditional debugging on each device would require maintaining separate devices and repeating test cases manually.
Perfect use cases for Appium:
- Cross-platform mobile apps – React Native and Flutter applications tested on iOS and Android
- Native mobile apps – Swift/Kotlin apps requiring native performance and OS features
- Hybrid applications – Cordova and Ionic apps with embedded webviews
- Mobile banking apps – Security-critical apps requiring comprehensive device testing
- Social media apps – Complex UI interactions across different device types
- E-commerce mobile apps – Payment flows on real devices with various screen sizes
Appium solves this by automating tests that run identically on both platforms.
Teams can test native mobile apps built with Swift or Kotlin, hybrid apps built with React Native or Flutter.
Key Advantages of Appium
Appium is completely free and open-source with zero licensing costs. It eliminates vendor lock-in concerns common with commercial QA automation tools. It enables cross-platform testing, allowing a single test script to run on both Android and iOS.
Distinct advantages for mobile teams:
- Cross-platform efficiency – Single test suite for iOS and Android reduces maintenance by 50%
- Zero licensing costs – Completely free with no commercial restrictions
- Multi-language support – Java, Python, Ruby, JavaScript, C#, PHP available
- All application types – Native, hybrid, and mobile web app support
- Real device testing – Physical devices, emulators, and simulators all supported
- Vendor agnostic – Works with any device, no manufacturer dependency
- Active development – Rapid updates supporting latest iOS and Android releases
The framework supports native, hybrid, and mobile web applications. Appium supports multiple coding languages through client bindings. The vendor-agnostic architecture means running tests on any device with appropriate drivers.
Comprehensive Comparison: Appium vs Selenium
Feature-by-Feature Analysis Matrix
| Parameter | Appium | Selenium |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Native, hybrid, and mobile web app automation | Web application automation across browsers |
| Target Platform | Mobile devices (iOS, Android, Windows) | Web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) |
| Founded Year | 2011 | 2004 |
| Supported Languages | Java, Python, Ruby, Node.js, JavaScript, C#, PHP | Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, C#, JavaScript, Go |
| Programming Skills | Intermediate to advanced | Intermediate to advanced |
| Cost Model | Completely free and open-source | Completely free and open-source |
| Device Coverage | Real devices, emulators, simulators | Real devices via cloud services |
| Browser Support | Mobile browsers only | Desktop browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) |
| Parallel Execution | Appium Server instances and Grid | Selenium Grid with unlimited scaling |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to steep | Moderate |
| Community Size | Large and growing | Extremely large and mature |
| Test Speed | Slower (10-20 seconds per test) | Faster (5-10 seconds per test) |
| Maintenance Burden | High (frequent updates) | Low to moderate |
| Best Use Case | Mobile app and cross-platform testing | Web application testing across browsers |
| Scalability | Limited by device availability | Unlimited horizontal scaling |
| Installation | Complex (requires mobile SDKs) | Simple (straightforward setup) |
1. Technical Architecture Differences
Selenium WebDriver communicates directly with browsers through their native drivers. It establishes direct connections to browser APIs and rendering engines.
This direct approach provides fast, reliable communication without intermediaries or translation layers.
Selenium advantages:
- Direct browser communication reduces latency significantly
- Access to native browser APIs and rendering engine features
- Faster test execution (5-10 seconds per test on average)
- Lower overhead from intermediary layers
- Simpler architecture for web-only testing
Appium Server acts as an intermediary between test scripts and mobile devices.
Appium’s architecture enables exceptional flexibility across different devices without requiring complete test rewrites.
Appium advantages:
- Single codebase for multiple platforms (iOS and Android)
- Flexible device testing without code changes
- Support for real devices and emulators
- Platform-agnostic approach avoiding vendor lock-in
- Easier maintenance for multi-platform apps
2. Language Binding and Ecosystem
Selenium has stronger community support for Java and Python, with extensive examples and libraries.
Selenium:
- Stronger Java community with TestNG integration
- Extensive Python libraries and pytest support
- More Stack Overflow answers and tutorials
- Better integration with CI/CD tools
- More commercial support options available
Appium similarly supports Java and Python but has equally strong Ruby and JavaScript support.
Appium:
- Excellent JavaScript/Node.js ecosystem
- Strong Ruby community for mobile testing
- WebdriverIO integration and support
- Growing Python community contributions
- Active maintenance and frequent updates
The JavaScript ecosystem is particularly strong for Appium, with excellent integration through WebdriverIO. Popular testing frameworks appeal to Node.js developers more than traditional QA engineers.
3. Element Locators and Selection Strategies
Selenium primarily uses CSS selectors and XPath to locate elements on web pages. CSS selectors typically offer better performance than XPath queries.
They are the preferred choice for modern web automation scripts.
Selenium locator options:
- CSS selectors – Best performance, preferred for modern debugging
- XPath – More flexible but slower than CSS
- ID locators – Fastest when available
- Class names – Good for styling-based elements
- Link text – Specific to hyperlink elements
Appium supports XPath, ID, class name, and accessibility IDs for element location. Appium’s support for accessibility identifiers provides more robust element location in well-designed apps.
Appium locator strategies:
- Accessibility IDs – Most stable, recommended for well-designed mobile apps
- XPath – Flexible but performance-heavy on mobile
- ID locators – Fast and reliable when available
- Class name – Available but less stable than web apps
- Predicate strings – iOS-specific locator strategy
4. Test Execution Speed and Performance
Selenium tests typically execute faster because direct browser communication reduces latency. A typical Selenium web test case completes in 5-10 seconds for simple interactions. This enables rapid feedback loops in continuous integration pipelines.
Selenium’s speed advantages:
- Direct communication – No intermediary overhead
- Browser optimization – Native browser features enhance performance
- Parallel scaling – Grid enables unlimited concurrent tests
- Minimal latency – Local or cloud browser communication is fast
Appium tests generally execute slower due to the server intermediary layer.
The same test on a mobile device might require 10-20 seconds. Physical devices or cloud-based mobile devices introduce additional network latency.
Appium’s performance considerations:
- Server overhead – Appium server adds processing latency
- Device communication – Mobile device network delays add up
- Real device testing – Physical devices slower than emulators
- Parallel limitations – Limited by available device capacity
5. Maintenance and Update Frequency
Selenium follows a predictable release cycle with major updates roughly every six months. The project has dedicated corporate backing ensuring long-term sustainability. Feature development aligns with modern web standards.
Selenium benefits:
- Predictable release schedule
- Long-term stability and planning certainty
- Browser vendor collaboration ensuring compatibility
- Corporate backing guarantees continued support
- Proven track record over 20+ years
Appium updates more frequently, often releasing new versions monthly or quarterly. Mobile platform updates from Apple and Google are incorporated quickly. Compatibility with the latest iOS and Android releases is ensured rapidly.
Appium advantages:
- Rapid iOS and Android support
- Quick bug fixes and patches
- Latest mobile platform features
- Active open-source community
- Modern mobile development practices
Strategic Recommendations: Choosing Your Framework
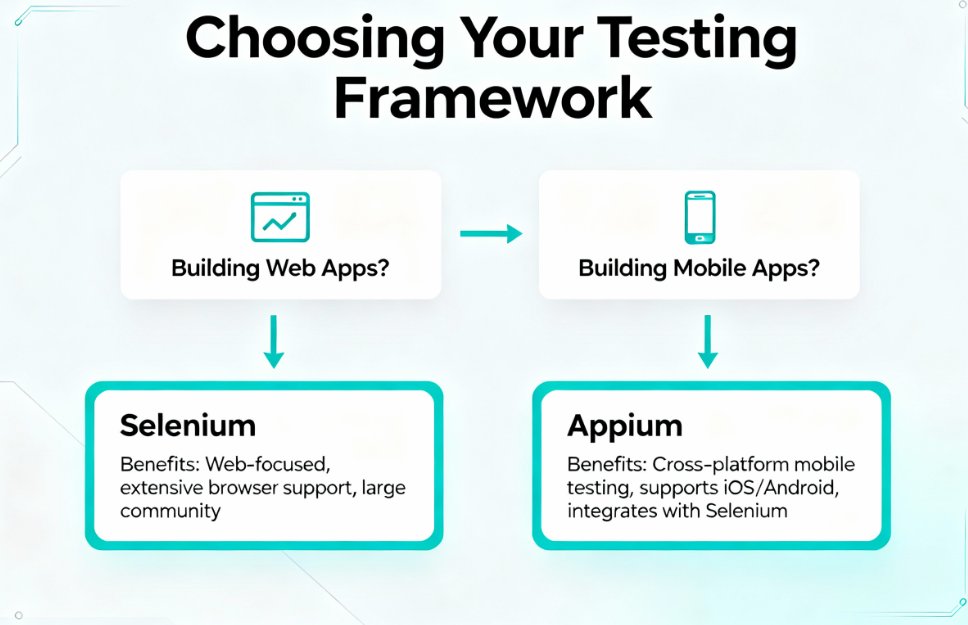
Comprehensive Selection Criteria
The choice between Appium and Selenium depends entirely on your application focus and debugging requirements.
If your primary product is a web application, Selenium is the clear choice. It provides superior speed, stability, and an exceptionally large community ecosystem.
Choose Selenium if you need:
- Cross-browser web application testing
- Testing across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge
- Responsive web design validation
- JavaScript-heavy application testing
- Maximum performance and scalability
- Largest community and support resources
- Mature, battle-tested framework
If you’re building native or hybrid mobile applications, Appium becomes essential. No viable alternative exists providing equal flexibility and cross-platform mobile coverage.
Choose Appium if you need:
- iOS and Android app automation
- Native Swift/Kotlin app testing
- React Native or Flutter testing
- Hybrid Cordova/Ionic app support
- Cross-platform test code reuse
- Real device and emulator testing
- Multi-platform consistency
The Other Choice: Panto AI
Panto AI addresses limitations inherent in both Selenium and Appium by operating above the traditional driver-based automation model. Instead of relying on brittle selectors or platform-specific test logic, Panto AI focuses on intent-driven testing, using AI to understand user flows, adapt to UI changes automatically, and maintain tests as applications evolve.
It introduces capabilities such as autonomous test generation from real user behavior, self-healing across web and mobile interfaces, and significantly reduced maintenance effort; areas where neither Selenium nor Appium provides native solutions.
Hybrid Approach: Using Both Frameworks
Organizations building both web and mobile versions use both frameworks in complementary fashion. Teams might use Selenium for web testing and Appium for mobile testing. This creates comprehensive testing strategy covering all user-facing applications.
Benefits of dual framework approach:
- Complete coverage – Web and mobile testing in single strategy
- Code reuse – Similar test patterns across frameworks
- Team efficiency – Developers use familiar languages
- Risk mitigation – Don’t bet on single framework
- Future flexibility – Easy to adapt to new platforms
This dual-framework approach requires slightly more training and tooling complexity. However, it provides the best coverage across your entire product ecosystem. Many enterprise organizations successfully manage both frameworks in their testing infrastructure.
Implementation tips:
- Use shared test data and utilities across frameworks
- Standardize naming conventions and best practices
- Maintain separate but similar test repositories
- Train team on both frameworks simultaneously
- Build CI/CD pipelines supporting both tools
Implementation Considerations
Consider your team’s coding language preferences when deciding between frameworks. If your team is skilled in Java with TestNG, Selenium integrates naturally. JavaScript-focused teams might find Appium’s strong Node.js support more convenient.
Key implementation factors:
- Language expertise – Java/Python better for Selenium, JavaScript better for Appium
- Existing infrastructure – Browser clouds for Selenium, mobile device clouds for Appium
- Team size and skills – Larger teams can support both frameworks easily
- Project timeline – Selenium has faster setup and learning curve
- Long-term vision – Consider future platform and application needs
Budget constraints typically don’t factor in since both tools are free. However, infrastructure costs matter significantly in long-term scaling decisions.
Cost considerations:
- Tool licensing – Both completely free
- Browser clouds – Sauce Labs, BrowserStack ($500-5000/month)
- Mobile device clouds – AWS Device Farm, BrowserStack ($1000-10000/month)
- Team training – Budget for workshops and certifications
- Infrastructure – Servers and CI/CD pipeline enhancements
Making the Final Decision
Start by identifying your debugging scope clearly and honestly assessing your needs. Create simple tests in both frameworks to evaluate the learning curve. Most teams find practical experience reveals which tool aligns better with their workflow.
Final decision checklist:
- ✓ Define primary application type (web vs mobile)
- ✓ Identify target platforms and browsers
- ✓ Assess team programming language skills
- ✓ Evaluate infrastructure and budget constraints
- ✓ Create proof-of-concept tests in both frameworks
- ✓ Consider long-term platform roadmap
- ✓ Review community support and resources
- ✓ Plan training and team development
The verdict is strategically straightforward: Selenium for web application testing, Appium for mobile testing. Many successful QA programs use both tools strategically in their respective domains. Leverage each framework’s considerable strengths for delivering quality at scale.
That said, teams seeking to move beyond script-heavy automation may choose Panto AI. It introduces AI-driven test creation and automatically adapts to UI changes across web and mobile applications. This reduces maintenance overhead while accelerating coverage and sustaining quality as products evolve.






